미숙 신생아들에게 모유수유나 인공영양을 먹일 때, Breastfeeding or formula feeding for premature newborn infants
미숙 신생아에게 모유를 수유할까 인공영양을 먹일 것인가
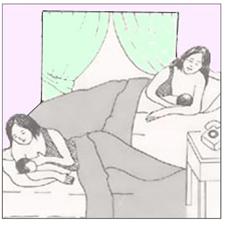
그림 4-41. 크고 건강한 미숙 신생아들에게 모유수유를 하는 방법은 만삭에 태어난 정상 신생아들에게 모유수유를 하는 방법과 별로 다를 바가 없다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 4-42. 아주 작은 미숙 신생아들에게 먹일 때는 이런 종류의 특수 인공영양 젖병을 이용할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 출생 시 체중이 2~2.5kg이거나 그 이상 나가는 건강하고 비교적 큰 미숙 신생아들에게 모유를 수유하는 방법이나 인공영양을 먹이는 방법은 만삭에 태어난 정상 신생아들에게 모유나 인공영양을 먹이는 방법과 별로 다른 바가 없다.
- 일반적으로 임신 35~37주에 태어난 미숙 신생아가 출생 후 전반적으로 건강하면 분만 후 바로 모유를 수유 할 수 있다. 또 모유수유를 하지 않고 인공영양을 먹이려면 바로 인공영양를 먹일 수 있다.
- 그러나 출생 시 체중이 2kg 이하 되는 작은 미숙 신생아나 저체중 신생아에게 모유수유를 하거나 인공영양을 먹이는 방법은 달라진다.
- 이런 미숙 신생아에게 모유수유를 하거나 인공영양을 먹이려면 더 많은 피딩 기술(Feeding techniques/영양법)과 지식이 필요하다.
- 때로는 의사나 간호사의 도움을 받아 인공영양을 먹이기도 하고 모유수유를 할 때도 있다.
- 임신 35~37주에 태어난 미숙 신생들 중 일부는 엄마의 젖꼭지를 어렵게 빨 수 있다.
- 이럴 때는 아기 스스로가 엄마의 젖꼭지를 빨아 모유를 잘 먹을 수 있을 때까지 수유모가 맨손으로 젖을 짜거나 유축기로 젖을 짜서 젖병에 담아 젖병으로 아기에게 엄마 젖을 먹일 수 있다.
- 출생 시 체중이 1.5kg 이하 되는 아주 작은 미숙 신생아의 대부분은 엄마의 젖꼭지나 우유병 꼭지를 제대로 빨 수 있는 힘조차 없다.
- 그래서 우유병 꼭지의 구멍이 좀 더 크게 뚫린 특수 우유병 꼭지로 인공영양을 먹이기도 하고 더 쉽게 먹을 수 있게 만든 미숙 신생아 전용 젖병을 이용해 먹이기도 한다.
- 때로는 손이나 유축기로 짠 모유나 인공영양을 피딩 튜브 기술(튜브 영양법) (사진4-11, 나-12참조)을 이용해 아주 작은 미숙 신생아들에게 짠 모유나 인공영양을 먹이기도 하고 특별하게 만든 우유병 꼭지를 이용해, 또는 특별하게 만든 젖병을 이용해 짠 모유를 먹이기도 한다.
- 모유는 비교적 소화가 잘되고 감염병을 예방하는 데 좋은 자연 음식물이기 때문에 가능한 미숙 신생아에게는 모유를 주로 먹이는 것이 좋다.
- 대부분의 미숙 신생아는 만삭 신생아에 비해 모유나 인공영양을 먹은 후 잘 넘길 수 있다.
- 때로는 생리적 위식도 역류로 먹은 모유 등을 잘 넘길 수 있다.
- 구토물이 기관 속이나 기관지 속, 폐 속으로 흡인될 수 있어 흡인성 폐렴이 더 쉽게 생길 수 있다. 이런 이유로 미숙 신생아를 양호하는 데는 더 많은 사랑과 인내, 관심과 육아지식이 더 필요하다.
| 아주 작은 미숙 신생아(극소 저 출생체중아)를 위한 모유나 인공영양 먹이기 |
Breastfeeding or formula feeding for very small premature infants
사진 4-43. 튜브 피딩(튜브 영양법). 아주 작은 미숙 신생아에게 짠 젖을 먹일 때는 특수 우유병 꼭지를 이용해 먹일 수도 있고 튜브 피딩(튜브 영양법)을 할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
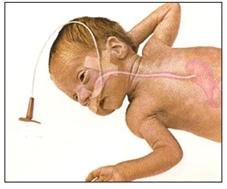
그림 4-44. 아주 작은 미숙 신생아에게 짠 젖을 먹일 때는 특수 우유병 꼭지를 이용해 먹이거나 튜브 피딩(튜브 영양법)을 할 수 있다. 피딩 튜브가 코-인두-식도-위로 들어가 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.이 튜브를 비위튜브라고도 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 태어난 첫 날부터 엄마의 젖꼭지나 우유병 꼭지를 스스로 빨아 먹을 수 없을 정도로 아주 작은 미숙 신생아도 있다.
- 이렇게 아주 작은 미숙 신생아를 ‘극소 저 출생체중아’라고 한다. 이런 아기들에게 출생한 첫 날부터 10% 포도당액 혈관주사로 영양공급과 수분을 공급하면서 아주 작은 미숙 신생아들이 스스로 젖꼭지를 빨아 모유나 인공영양을 먹을 수 있는지 알아본다.
- 이렇게 알아보는 동안, 엄마의 젖꼭지나 우유병 꼭지를 힘차게 빨아먹을 수 있으면 엄마의 젖꼭지를 직접 빨아 젖을 먹게 시도 해 본다.
- 그러면서 아주 작은 미숙 신생아가 쉽게 빨아먹을 수 있도록 특별하게 만든 우유병 꼭지로 인공영양을 먹인다.
- 그러나 대부분의 아주 작은 미숙 신생아들은 태어난 후 얼마동안 그들 스스로 엄마의 젖꼭지를 빨아 모유나 인공영양을 먹을 수 없다.
- 만일 아주 작은 미숙 신생아가 엄마의 젖꼭지를 빨아 엄마의 젖을 먹을 수 있으면 만삭 신생아에게 젖을 먹이는 방법과 거의 같은 방법으로 젖을 먹이기 시작 한다.
- 반면, 아주 작은 미숙 신생아가 엄마의 젖꼭지나 우유병 꼭지를 빨아 먹을 힘도 없으면 짠 엄마의 젖이나 인공영양을 작은 피딩 튜브(Feeding Tube)를 통해 먹이기도 한다.
- 이렇게 피딩 튜브로 먹이면서 때때로 우유병 꼭지를 빨려 인공영양을 먹여도 보고 엄마의 젖꼭지를 직접 빨려 엄마의 젖도 먹여 본다.
- 미숙 신생아가 스스로 엄마의 젖꼭지를 빨아 엄마의 젖을 먹을 수 있거나 인공영양을 우유병 꼭지를 빨아 먹을 수 있고, 체중이 점점 정상적으로 늘어나는 등 전반적으로 건강하게 성장발육하면 더 이상 피딩 튜브로 먹이지 않아도 된다.
- 대신 미숙 신생아가 엄마의 젖꼭지나 우유병 꼭지를 스스로 입으로 직접 빨아 젖이나 인공영양을 먹도록 한다.
- 그 이후에는 만삭으로 태어난 건강한 신생아들에게 모유를 먹이는 방법과 인공영양을 먹이는 방법과 거의 같게 미숙 신생아들에게도 먹일 수 있다.

사진 4-45. 인공영양을 먹일 때 필요한 것들
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 4-46. 인공영양을 먹일 때 쓸 수 있는 여러 종류의 우유병들과 우유병 꼭지
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

사진 4-47.저체중 신생아들이나 미숙 신생아들에게 먹일 수 있는 특수 인공영양과 젖병
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
사진 4-48. 저체중 신생아들이나 미숙 신생아 들에게 먹일 수 있는 특수 인공영양
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
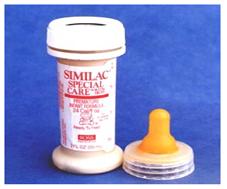
사진 4-49. 아주 작은 미숙 신생아들이나 저체중 신생아들에게 고 칼로리 포물라를 먹일 수 있다. 고 칼로리 포물라의 30cc에서 24킬로칼로리의 열량이 나올 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
때로는 미숙 신생아들에게 인공영양을 쉽게 먹일 수 있게 만든 특수 우유병 꼭지로 인공영양을 먹이거나 특수 인공영양을 먹이기도 한다.
Breastfeeding or formula feeding for premature newborn infants 미숙 신생아들에게 모유수유나 인공영양을 먹일 때
- Whether to breastfeed or feed a premature newborn baby with artificial nutrition-formula

Figure 4-41. The method of breastfeeding large, healthy premature newborns is no different from the method of breastfeeding normal newborns born at full term. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 4-42. This kind of special artificial nutrition bottle can be used when feeding very small, premature newborns. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- The method of breastfeeding or feeding artificial nutrition to healthy and relatively large infants weighing 2~2.5kg or more at birth differs from the method of feeding breastmilk or artificial nutrition to normal newborns born at full term.
- In general, immature newborns born at 35-37 weeks of gestation can breastfeed immediately after delivery if they are generally healthy after birth.
- Also, if you want to feed artificial nutrition without breastfeeding, you can feed artificial nutrition immediately.
- However, the method of breastfeeding or feeding artificial nutrition to small immature or underweight newborns weighing less than 2kg at birth is different.
- Breastfeeding or feeding artificial nutrition to these premature newborns requires more feeding techniques and knowledge.
- Sometimes, with the help of a doctor or nurse, they are fed artificial nutrition and sometimes breastfeed.
- Some of the immature newborns born between the 35th and 37th weeks of gestation can have a difficult time sucking their mother’s nipples.
- In this case, the nursing mother can breastfeed the baby with a bottle by milking it with her bare hands, or milking it with a breast pump until the baby is able to suck the mother’s nipples and feed her breasts well.
- Most of the very small, premature newborns weighing less than 1.5 kg at birth do not even have the power to properly suck the mother’s nipple or bottle nipple.
- Therefore, artificial nutrients are fed with a special milk bottle teat with a larger hole in the milk bottle teat, or a baby bottle exclusively for immature newborns is used to make it easier to eat.
- Sometimes, breast milk or artificial nutrition squeezed by hand or breast pump is fed to very small immature newborns using the feeding tube technology (tube nutrition method) (refer to photo 4-11, b-12), and specially made milk
- You can also feed the breast milk squeezed from the top of the bottle or from a specially made baby bottle. Breast milk is a relatively well-digested and natural food that is good for preventing infectious diseases, so breastfeeding is recommended for premature newborns as much as possible.
- Most immature newborns are better able to pass after breast milk or artificial nutrition than full-term newborns.
- Sometimes, physiological gastroesophageal reflux can pass through breast milk that has been eaten. Vomit and then aspirate into the trachea, bronchi, or lungs, making it easier to develop aspiration pneumonia. For this reason, better love, patience, attention, and parenting knowledge are needed to keep a premature newborn baby in good condition.
Breast milk or artificial nutrition for very small premature newborns (very low birth weight)
- Breastfeeding or formula feeding for very small premature infants

Photo 4-43. Tube feeding (tube nutrition). When feeding squeezed milk to a very small immature newborn baby, it can be fed with a special milk bottle nipple or tube feeding (tube nutrition). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 4-44. When feeding squeezed milk to a very small immature newborn, it can be fed with a special milk bottle tip or tube feeding (tube nutrition). You can see that the feeding tube goes into the nasopharynx, esophagus, and stomach, which is also called the nasogastric tube. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- Some immature newborns are so small that they cannot suck their mother’s nipples or milk bottle nipples from the first day of their birth.
- Such very small immature newborns are called ‘very low birth weight’. From the first day of birth to these babies, 10% glucose vascular injection is used to supply nutrition and hydration.
- While examining this way, if they can suck the mother’s nipple or the teat of the milk bottle vigorously, try to suck the mother’s nipples and breastfeed.
- At the same time, artificial nutrients are fed with a special milk bottle nipple that can be easily sucked by very small immature newborns.
- However, most tiny immature newborns are unable to feed on breast milk or artificial nutrition by themselves sucking on their mother’s nipples for some time after birth. If a tiny, immature newborn can suck on her mother’s nipples and feed her mother’s milk, she begins to breastfeed her in much the same way she breastfeeds her full-term newborn.
- On the other hand, when a very small, immature newborn has no power to suck the mother’s nipples or milk bottle nipples, she may feed her squeezed mother’s milk or artificial nutrition through a small feeding tube.
- While feeding with a feeding tube like this, they sometimes suck the bottle’s teat to feed formula and try to suck the mother’s nipples directly to feed the mother’s milk. Inexperienced newborns can suck their mother’s nipples and feed their mother’s milk, or artificial nutrition can be sucked through the teat of a milk bottle, and when the overall healthy growth and development, such as gradually gaining weight, can no longer be fed with a feeding tube.
- Instead, an immature newborn baby sucks her mother’s nipples or the teat of a milk bottle directly into her mouth, allowing them to feed on breast milk or artificial nutrition. After that, it can be fed to immature newborns in much the same way as breastfeeding and artificial nutrition to healthy newborns born in full term.

Photo 4-45. What you need when feeding artificial nutrition. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 4-46. Several types of milk bottles and bottle caps can be used when feeding artificial nutrition. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 4-47: Special artificial nutrition and feeding bottle that can be fed to underweight newborns or premature newborns. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 4-48. Special artificial nutrition that can be fed to underweight or premature newborns. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 4-49. High-calorie formulas can be fed to very small, premature, and underweight newborns. A high-calorie formula can produce 24 kilocalories in 30cc. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Sometimes, artificial nutrition or special artificial nutrition is fed with a special milk bottle nipple made to make it easy to feed artificial nutrition to immature newborns.
출처 및 참조 문헌
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
|
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP 미국 소아과 전문의, 한국 소아청소년과 전문의 이상원 저 “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다. “The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.” |