서혜부 탈장(서혜 헤르니아/서혜 탈장)과 서혜부 탈장 감돈, Inguinal hernia and Inguinal hernia strangulation
| 서혜부 탈장(서혜 헤르니아/서혜 탈장)의 개의 |
- 횡격막 헤르니아(Diaphragmatic hernia/가로막이탈), 직접 샅굴 헤르니아(Direct inguinal hernia), 간접 서혜 탈장(Indirect inguinal hernia), 직접 서혜 탈장(Direct inguinal hernia), 원반 탈출증(Herniated disc), 추간판 탈출증, 궁둥구멍 탈장(Sciatic hernia), 좌골공 탈장(Scrotal hernia), 음낭 헤르니아(Sliding hiatal hernia), 양측성 서혜부 탈장 등 여러 종류의 탈장 및 헤르니아가 신체 여러 부위에 생길 수 있다.
- 서혜부 탈장은
-
- 간접형 서혜부 탈장과
- 직접형 서혜부 탈장 두 가지로 나누고
- 일측성 서혜부탈장 또는
- 양측성 서혜부 탈장으로도 나누고,
- 또 선천성 완전 서혜부 음낭 탈장도 있다.
- 임신 6~7개월까지 양쪽 고환은 태아의 복강 내에 있는 것이 보통이다.
- 그 후 양쪽 고환이 태아 복강 내에서 서혜관 속을 통과해 음낭 속으로 나와 있다.
- 그 후부터 태아 고환이 음낭 속에 계속 머물러 있는 것이 정상이다.
- 그리고 복강 속에 있던 고환이 서혜관 속을 통과한 후 음낭 속으로 내려온 후에는 서혜관이 완전히 막히는 것이 정상이다.
- 때로는 한쪽 서혜관 속이나 양쪽 서혜관 속이 막히지 않을 수 있다.
- 이 때 복강 내 복막의 일부나, 여성인 경우 난소, 또는 장관의 일부가 막히지 않은 서혜관 속을 통과해 복벽 밖에 있는 대음순 속으로 나올 수 있고,
- 남성인 경우에는 복강 내 복막의 일부, 장관의 일부가 서혜관 속을 통과하여 음낭 속, 또는 음낭의 바로 위에 있는 서혜관 속 등으로 빠져 나올 수 있다. 이것을 간접형 서혜부 탈장이라고 한다. 간접형 서혜부 탈장은 여아들에게보다 남아들에게 더 잘 생긴다. 다음은 간접형 서혜부 탈장에 대해서 주로 설명한다. (그림47 참조)
| 서혜부 탈장(서혜 헤르니아/서혜 탈장)의 원인 |
- 원인은 아직도 확실히 모른다.
- 서혜부 탈장은 만삭 신생아들의 1~5%, 미숙 신생아들의 9~10%에게 발생한다.
- 아주 더 작은 미숙 신생아에게는 그 보다 더 많이 발생한다.
- 남아와 여아의 서혜부 탈장의 발생 비율은 5:1이다.
- 서혜부 탈장의 60%는 우측에 생기고 10%는 양측성이다(출처; Contemporary pediatrics, December 2008. p.516).
- 고환이 음낭 속에 없이 태어난 신생아들은 서혜부 탈장 이외 다른 종류의 선천성 기형을 갖고 태어날 수 있다.
- 직접형 서혜부 탈장보다 간접형 서혜부 탈장이 소아청소년들에게 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
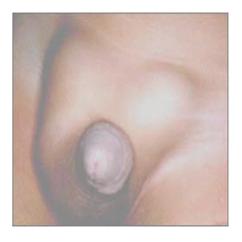
사진 234. 유아 양쪽 서혜부에 있는 간접형 서혜부 탈장
탈장으로 인해 양쪽 서혜부가 볼록해 보인다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
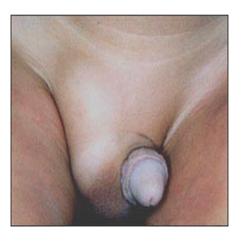
사진 235. 잠시 후 왼쪽 간접형 서혜부 탈장 내용물이 복강 내로 들어가서 왼쪽 서혜부는 정상적으로 보이나 오른쪽 서혜부 속에 그대로 있는 서혜부 탈장으로 인해 볼록하게 보인다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
| 서혜부 탈장(서혜 헤르니아/서혜 탈장)의 증상 징후 |
- 증상 징후는 다양하다.
- 서혜부 탈장이 출생 시 신생아에게 나타날 수도 있고 첫 돌이 오기 전 영아기에 나타날 수도 있다.
- 장관의 일부분, 복막의 일부분, 또는 난소 등이 서혜부 속, 서혜부 바로 아래부위 속, 사타구니 속 음낭 속 또는 대음순 속으로 나와 간접형 서혜부 탈장이 생길 수 있다.
- 이 때 탈장으로 서혜부가 불쑥 나온 것을 육안으로 볼 수 있다(사진 234, 235 참조).
- 탈장 속에 들어 있는 장관의 일부분이나 복막의 일부분으로 서혜부가 불룩하게 나올 수 있고 피부 아래에 있는 탈장 내용(Hernia contents)물을 손으로 만져볼 수 있다.
- 서혜부 탈장 속에 나와 있는 장관의 일부분이나 복막의 일부분의 크기에 따라 서혜부 탈장의 크기가 다르다.
- 서혜부 탈장은 밤알만 한 것도 있고 달걀만 한 것도 있다.
- 서혜부 탈장이 있을 때 장관의 일부분이나 복막의 일부분이 복강 내에서 서혜관 속을 통과해 서혜부 속이나 대음순 속, 음낭 속, 음낭 속 바로 윗부분 서혜관 속으로 빠져 나온 후 아무 증상이 없이 그대로 얼마동안 있다가 탈장된 장관의 일부나 복막의 일부가 복강 내로 다시 들어간후 얼마 동안 그 상태로 있을 수 있다(사진 235 참조).
- 이와 같이 복강 내로 들어갔던 탈장 내용물이 복강 밖 서혜관 속으로 다시 나왔다가 복강 속으로 다시 들어갔다 나왔다 할 수 있다.
- 다시 설명하면, 서혜부 탈장 내용물이 서혜관 속을 통과해서 복강 내로, 다시 들어갔다가 복강 외 서혜부 속으로 다시 나오는 식으로 서혜부 탈장 내용물이 들락날락한다.
- 특히 서혜부 탈장이 있는 신생아, 영유아가 울 때나 대변을 보기 위해 배에 힘을 많이 주면 복강 내압이 증가될 때, 대변을 보기 위해서 복강 속에 힘을 많이 줄 때, 또는 기침할 때 복강 내압이 증가될 때 복강 속으로 들어가 있던 서혜부 탈장 내용물이 복강 속 밖에 있는 서혜관 속으로 다시 나올 수 있고, 또 이미 복강 내에서 서혜관 속으로나 음낭 속으로 나와 있던 탈장 내용물이 더 커지기도 하고 서혜부나 음낭이 볼록하게 커지는 것이 보통이다.
- 서혜부 탈장이 있는 환아가 가만히 누워 휴식을 취하거나, 잠잘 때에는 서혜부 탈장 속에 있던 탈장 내용물이 복강 속으로 다시 들어가 있을 수 있다.
- 육체적으로 매우 활동적 사춘기 아이에게 있는 서혜부 탈장의 내용물이 서혜관 속으로 나온 후 그 탈장 내용물이 더 이상 복강 속으로 들어가지 않고 서혜관 속에 계속 머물러 있는 경우도 있다.
- 서혜부 탈장이 있을 때 서혜관 속에 나온 장관의 일부나 복막의 일부 또는 난소 등이 복강 속으로 들어갔다 서혜관 속으로 나왔다 하는 것이 보통이지만, 복강 속 바깥에 있는 서혜관 속으로 일단 나왔던 탈장 내용물이 또다시 복강 내로 더 이상 저절로 들어가지 못할 때가 있다.
- 손가락으로 그 탈장 내용물을 복강 내로 살짝 밀어 넣어도 탈장 내용물이 복강 내로 더 이상 들어가지 않을 때도 있다. 이런 경우를 서혜부 헤르니아(서혜부 탈장)가 감돈되었다고 한다. 이 병을 헤르니아 감돈이라고 한다.
- 서혜부 탈장이 감돈 되었을 때에는 서혜관 속으로 나온 복막의 일부분이나 장관의 일부분 등의 탈장 내용물의 혈액 순환이 정상적으로 되지 않기 때문에 탈장 내용물이 괴사될 수 있고 손상될 수 있다.
- 이 때 장폐색증이 생길 수 있고 그에 따른 증상 징후가 생길 수 있다. 심한 복통과 구토가 생길 수 있다.
- 신생아에게 생긴 서혜부 탈장은 더 쉽게 감돈 될 수 있다.
- 서혜부 탈장이 감돈 되었을 때에는 응급 수술로 치료하지 않으면 생명에도 위험할 수 있다.
| 서혜부 탈장(서혜 헤르니아/서혜 탈장)의 진단 |
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병을 진단한다.
- 서혜부 탈장 내용물은 서혜관 속을 통해 복강 속으로 들어갔다 복강 속 밖으로 나왔다 하는 것이 보통이다.
- 탈장 내용물이 복강 속으로 들어가 있는 동안에 진찰을 받을 때는 서혜부 탈장이 있는지 없는지 그냥 보고서 확실히 알 수 없는 때도 있다.
- 그러나 진찰을 받을 때 배에 힘을 많이 주면 복강 내압이 높아지고 복강 내 탈장 내용물이 서혜관 속으로 나온 서혜부 탈장 현상을 다시 볼 수 있고 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
| 서혜부 탈장(서혜 헤르니아/서혜 탈장)의 치료 |
- 서혜부 탈장 내용물이 복강 내로 쉽게 들어갔다 나왔다 하고 아무 증상 징후가 없어도 적절한 시기를 선택해 선택적 수술 치료를 한다.
- 특히 신생아들이나 영유아들의 서혜부 탈장증은 가능한 한 속히 선택적 수술 치료를 해 주는 것이 좋다.
- 서혜부 탈장이 감돈되면 응급 수술 치료를 해야 한다.신생아의 식도, 위, 소장, 대장 등의 폐쇄증. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제 6권 신생아 성장 발육 양호 및 질환-신생아 외음부 참조.
|
다음은 “산전 초음파 검사와 신생아 소장폐쇄 ”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 산전 초음파 검사와 신생아 소장폐쇄 관하여
Q.
안녕하세요? 답답한 마음에 글을 올립니다.
저는 임신 28주째 접어든 예비엄마입니다. 27주째 아기의 장 쪽이 이상하다해서 정밀 초음파를 받았습니다. 결과로 소장폐색이라고 나왔는데,, 양수를 삼키지 않아 지금은 양수가 조금 많은 편이며,,앞으로 더 많아질 듯 하다고 합니다. 그리고, 콩팥 쪽에 소변? 이 좀 고여 있다고 합니다. 그리고 아기가 주수보다 약간 작다고 합니다. 소아청소년과 전문선생님과는 아직 상담한 적은 없지만,, 수술을 해야 한다고 하네요. 남들 일처럼 생각했는데,, 건강한 아기를 출산하지 못 하는 점에 무척 죄책감과 아기에게 미안한 마음만 들어 눈물밖에 나질 않습니다. 그리고,, 태어난 즉시 수술을 해야 하나요? 조그만한 아기가 견딜 수 있을까요? 그리고,,수술시간과,,, 수술 후 아기의 상태는 어떻게 되나요? 제가 할 수 있는 일은 없는지,,,, 여러 가지 궁금한 점들이 많습니다.
약한 아기 만들지 않으려고 열심히 먹고 있습니다. 선생님경험으로 저의 아기상태가 어떤 쪽에 속하나요?? 그리고 뇌나 다른 곳은 문제가 없다고 하는데,, 양수가 많으면 아기에게 가져다주는 영향이 생길 수 있나요? 바쁘시지만,, 자세한 답변 부탁드립니다.
A.
진이님
안녕하세요. 답변이 늦어서 죄송합니다. 지금쯤은 궁금하셨던 문제에 관한 답변을 얻으셨으리라 믿습니다.
저는 일반 소아청소년과 전문의로서 태아의 질병에 대한 경험은 그렇게 많지는 않습니다.
그러나 질문하신 문제에 대해서 제 힘껏 말씀 드리겠습니다.
우선 출생 이후 신생아들이나 영유아들의 신체의 어떤 부분을 검사한 울트라사운드 검사의 결과가 항시 옳을 수 없습니다.
똑같은 X선 촬영 사진 하나를 여러 방사선과 전문의들이 판독할 때 그 판독 결과가 때로는 많은 차이 날 수 있습니다.
저도 자녀의 산전 초음파 검사 결과가 전부 옳지 않기를 간절히 빕니다.
다음 정보를 참조하시기를 바랍니다.
Inguinal hernia and Inguinal hernia strangulation 서혜부 탈장(서혜 헤르니아/서혜 탈장)과 서혜부 탈장 감돈
Inguinal hernia review
- There are many kinds of hernia such as Diaphragmatic hernia, direct inguinal hernia, indirect inguinal hernia, herniated disc, intervertebral disc herniation, Sciatic hernia, Scrotal hernia, Sliding hiatal hernia, bilateral inguinal hernia, etc. Several types of hernias can occur in various parts of the body.
Inguinal hernia
- Indirect inguinal hernia
- Divided into two types of direct inguinal hernia
- Unilateral inguinal hernia
- or Also divided into bilateral inguinal hernia,
- There is also a congenital complete inguinal scrotal hernia.
- By 6-7 months of pregnancy, both testicles are usually in the abdominal cavity of the fetus.
- After that, both testicles pass through the groin tube in the fetal abdominal cavity and come out into the scrotum.
- From then on, it is normal for the fetal testicles to remain in the scrotum. And after the testicles in the abdominal cavity pass through the groin tube(inguinal canal) and descend into the scrotum, it is normal for the groin tube to be completely blocked.
- Sometimes, the inside of one inguinal canal or both of them may not be blocked.
- At this time, a part of the peritoneum in the abdominal cavity or, in the case of a woman, the ovary or part of the intestine may pass through an unblocked groin tube and come out into the labia majora outside the abdominal wall.
- In males, a part of the peritoneum in the abdominal cavity and a part of the intestine may pass through the groin duct and exit into the scrotum or into the groin duct located directly above the scrotum.
- This is called an indirect inguinal hernia.
- An indirect inguinal hernia is more common in boys than in girls. The following mainly describes indirect groin hernia. (See Figure 47)
Causes of inguinal hernia
- The cause is still unknown. Inguinal hernias occur in 1-5% of full-term newborns and 9-10% of immature newborns.
- It occurs even more in very small, premature newborns.
- The incidence ratio of inguinal hernia in boys and girls is 5:1. 60% of inguinal hernias occur on the right side and 10% are bilateral (source; Contemporary pediatrics, December 2008. p.516).
- Newborns with no testicles in the scrotum may be born with other types of congenital anomalies other than an inguinal hernia.
- Indirect groin hernias are more likely to develop in children and adolescents than direct groin hernias.

Photo 234. Indirect inguinal hernia in both groin areas of infants. Both groin areas appear convex due to hernia. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

- Photo 235. After a while, the contents of the left indirect inguinal hernia enters the abdominal cavity, and the left groin is seen normally, but it looks convex due to the inguinal hernia remaining in the right groin. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Symptoms Signs of a groin hernia
- Symptoms, signs vary. An inguinal hernia may appear in newborns at birth or in infancy before the first birth.
- Part of the intestinal tract, part of the peritoneum, or ovaries may come into the groin, just below the groin, into the scrotum, or into the labia majora, resulting in an indirect inguinal hernia.
- At this time, it is possible to see with the naked eye that the groin protrusion was protruded due to a hernia (see photos 234 and 235).
- Part of the intestinal tract or peritoneum in the hernia can cause a bulge in the groin, and the hernia contents under the skin can be touched by hand. The size of the inguinal hernia differs depending on the size of the part of the intestine or the part of the peritoneum in the inguinal hernia.
- Some inguinal hernias are chestnut-sized and some are only an egg. When there is an inguinal hernia, part of the intestinal tract or part of the peritoneum passes through the inguinal canal from the abdominal cavity and exits into the groin tract, the labia majora, the scrotum, and the scrotum immediately above the groin, and then stays there for a while without any symptoms.
- Part of the intestinal tract or part of the peritoneum may remain in that state for some time after re-entering the abdominal cavity (see photo 235).
- In this way, the contents of the hernia that went into the abdominal cavity may be said to come out of the abdominal cavity and into the groin and then into and out of the abdominal cavity.
- In other words, the contents of the inguinal hernia go in and out of the inguinal hernia in such a way that the contents of the groin hernia pass through the groin tube, enter the abdominal cavity, and then re-enter into the groin outside the abdominal cavity.
- In particular, when newborns and infants with an inguinal hernia cry or when a lot of pressure is applied to the stomach to see stool, when the intra-abdominal pressure increases, when the pressure in the abdominal cavity increases to obtain a stool, or when coughing.
- The contents of the inguinal hernia that had entered the abdominal cavity may come out again into the groin duct outside the abdominal cavity, and the contents of the hernia that had already come into the groin or scrotum from the abdominal cavity become larger, and the groin or scrotum is usually convexly enlarged.
- When a child with an inguinal hernia lies still and rests, or when sleeping, the contents of the hernia in the inguinal hernia may reenter the abdominal cavity. In some cases, after the contents of the inguinal hernia in a physically active adolescent child come out into the groin, the contents of the hernia no longer enter the abdominal cavity and remain in the groin.
- When there is inguinal hernia, it is common to say that part of the intestinal tract, part of the peritoneum, or ovary from the intestinal tract enters the abdominal cavity and then comes out into the groin, but the contents of the hernia that once came out into the inguinal canal outside the abdominal cavity are further into the abdominal cavity.
- There are times when you can’t go in on your own.
- Sometimes the hernia contents can no longer enter the abdominal cavity even when the contents of the hernia are gently pushed into the abdominal cavity with a finger.
- In this case, it is said that the inguinal hernia (groin hernia) was confined.
- This disease is called Hernia strangulation.
- When the inguinal hernia is strangulated, the hernia contents may be necrotic and damaged because of the blood circulation of the hernia contents such as a part of the peritoneum or a part of the intestine that has come out into the inguinal tract is not normal.
- At this time, intestinal obstruction may occur and symptoms may occur. Severe abdominal pain and vomiting can occur. Inguinal hernias in newborns can be more easily strangulated.
- When an inguinal hernia is strangulated, it can be dangerous to life if not treated with emergency surgery.
Diagnosis of inguinal hernia
The disease is diagnosed by synthesizing the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings.
It is common that the contents of the inguinal hernia enter the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal and come out of the abdominal cavity.
When the contents of the hernia are in the abdominal cavity, there are times when you are not sure if you have a groin hernia or not.
However, if a lot of power is applied to the stomach during a medical examination, the intra-abdominal pressure increases and the inguinal hernia phenomenon in which the contents of the hernia in the abdominal cavity come out into the groin can be seen again and can be easily diagnosed.
Treatment of inguinal hernia
- Even if the contents of the inguinal hernia easily enter and exit the abdominal cavity, and there are no signs, symptoms, select an appropriate time for selective surgical treatment.
- In particular, it is recommended to provide selective surgical treatment for inguinal hernia in newborns or infants as soon as possible.
- If the inguinal hernia is confined, emergency surgical treatment is required: atresia of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine in newborns.
- Visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 6 Newborn’s Growth and Development Good and Diseases-Newborn’s Vulva.
The following is an example of online pediatric and adolescent health counseling questions and answers on “prenatal ultrasound and small bowel obstruction”.
Q&A.
Prenatal ultrasound and newborn small intestine obstruction
Q
. Good morning? I write in a frustrated heart. I am a prospective mother who has entered the 28th week of pregnancy. At the 27th week, the baby’s intestines were abnormal, so I received a precision ultrasound.
As a result, it turned out that it is an obstruction of the small intestine, but it is said that amniotic fluid is a little bit large now because amniotic fluid is not swallowed, and it is likely to increase in the future.
And, urine on the kidney side? It is said that this is a little stagnant. And it is said that the baby is a little smaller than her weeks.
I haven’t consulted with the pediatrics and adolescents department teacher yet, but they say they need surgery.
I thought of it like everyone else’s, but I only tear up because I feel very guilty and sorry for the baby for not being able to give birth to a healthy baby.
And,, do I have to undergo surgery immediately after I am born?
Can a little baby bear it?
And, the operation time and, what is the baby’s condition after the operation? I have a lot of questions about whether there is anything I can do about it. I am eating hard to avoid making a weak baby.
From the experience of the teacher, what is my baby’s condition? And it is said that there is no problem with the brain or other places, but if there is a lot of amniotic fluid, can it have any effect on the baby?
You are busy, but please give me a detailed answer.
A.
Jinyi Good morning. Sorry for the late reply. I am sure you have gotten the answers to the questions you have been curious about by now. As a general pediatrician, I don’t have much experience with fetal diseases.
However, I will tell you my best about the question you asked. First of all, the results of the Ultrasound test, which examines any part of the body of newborns or infants after birth, cannot always be correct.
When multiple radiologists read the same X-ray picture, the reading results can sometimes vary a lot.
I also sincerely hope that the results of my child’s prenatal ultrasound are not all correct. Please refer to the following information.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.