신생아 B형 간염, Neonatal hepatitis B
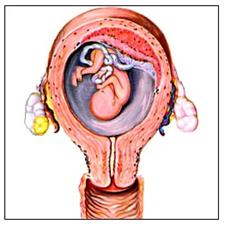
그림 150.임신 중 자궁 내 태아는 모체가 가지고 있는 B형 간염바이러스에 잘 감염되지 않다. 그러나 B형 간염바이러스를 보균하거나 B형 간염을 앓는 엄마가 분만 중 아기가 엄마로부터 B형 간염바이러스에 감염되어 신생아 B형 간염에 걸릴 수 있다.
출처-소아 가정의학백과 와 “Illustrations from Pregnancy in Anatomical Illustrations apear courtesy of the copyright owner c Carnation Company, Los Angeles, CA 1962“
사진 151. B형 간염바이러스를 보균하거나 B형 간염을 앓는 엄마가 분만 중 아기가 엄마로부터 B형 간염바이러스에 감염되어 신생아 B형 간염에 걸릴 수 있다.
그러나 임신 중 자궁 내 태아는 모체가 가지고 있는 B형 간염바이러스에 잘 감염되지 않는 것이 보통이다.
Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
- 신생아 황달에서 신생아 간염에 관해 이미 설명했으나 여기에서 다시 설명한다.
- 자궁 내에서 태아가 풍진바이러스, 사이토메갈로바이러스, 콕삭키바이러스, 또는 헐피스바이러스 등에 감염될 수 있다. 그 바이러스 감염으로 태아 간염이 생길 수 있다. 태아 간염이 출생 후 신생아 간염으로 이어질 수 있다.
- 출생 중 임신부로부터 태아가 A형 간염 바이러스나 B형 간염 바이러스에 감염되어 신생아에게 A형 간염이나 B형 간염이 생길 수 있다.
- 그런 간염의 증상 징후나 징후가 신생아기 이후 영유아기에 처음으로 나타 날 수 있다.
- 풍진바이러스, 사이토메갈로바이러스, 콕삭키바이러스, 헐피스바이러스, A형 간염 바이러스와 B형 간염바이러스, 톡소플라즈마 원충, 또는 매독균 등 병원체에 태아나 신생아가 감염될 때 신생아 간염이 생길 수 있다.
- 그 중 신생아 간염의 주원인은 B형 간염 바이러스이다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다- 소아가정간호 백과]-제 7권 소아청소년 감염병-매독 참조.
| 신생아가 B형 간염 바이러스에 감염되는 경로 |
- B형 간염바이러스를 보균한 여성들이 임신되면 B형 간염바이러스가 태반을 통해 태아에게로 감염될 수 있다.
- B형 간염을 앓고 있는 임신부로부터 B형 간염바이러스가 태반을 통해 태아에게 직접 감염될 수도 있고
- 분만 중 B형 간염바이러스가 태어나는 아기에게 직접 감염될 수 있고
- 출생 후 갓 태어난 신생아, 그 이후 신생아, 또는 그 후 영아가 산모로부터 감염될 수 있고
- 수혈 등으로 감염되기도 한다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다- 소아가정간호 백과]-제 7권 소아청소년 감염병-B형 간염 참조.
| 신생아 b형 간염의 증상 징후 |
- 임신 7~9개월경에 태아가 엄마가 가지고 있는 B형 간염 바이러스에 감염되어 태아가 B형 간염에 걸리면 조산될 수 있다.
- 신생아가 B형 간염 바이러스에 감염될 때 그 신생아는 급성 간염, 또는 만성 간염에 걸릴 수 있고, 심한 경우, 신생아 간염으로 사망할 수 있다.
- B형 간염을 앓는 대부분의 신생아는 B형 간염 바이러스 보균자가 될 수 있다.
- B형 간염을 심하게 앓으면 성장 발육이 지연될 수 있고 먹는 것도 시원치 않으며 배가 부르고 황달에 걸릴 수 있고 소변이 노랗게 된다.
| 신생아 b형 간염의 진단 |
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 엄마가 B형 간염 바이러스를 보균하고 있는지, 현재 B형 간염을 앓고 있는지, 또 과거에 앓은 경험이 있는지를 알아본다.
- B형 간염 바이러스의 항원과 항체가 있나 피검사를 하고, 신생아의 피에서 B형 간염 바이러스, 항원, 항체, 간 기능검사, CBC 피검사, 직접형 빌리루빈과 간접형 빌리루빈 검사를 하여 확진한다.
| 신생아 b형 간염의 치료 |
- 성인 만성 B형 간염은 Interferon-alfa, Lamivuden, Adefovir 등 항 바이러스제로 치료하나,
- 신생아 간염 치료에 아직도 특효약은 없다.
- 증상 징후에 따라 치료한다.
- B형 간염바이러스를 보균한 엄마나, 또는 B형 간염을 앓고 있는 엄마에게 태어났지만 그 아기가 B형 간염에 걸리지 않았으면 그 아기에게 모유를 수유해서는 안 된다.
- 그 신생아가 엄마로부터 B형 간염바이러스에 감염되지 않도록 출생 후 곧 B형 간염 백신으로 예방접종을 해주고 B형 간염 면역글로불린 주사를 맞아 예방적 치료를 한다.
- 이런 경우는 모유를 수유할 수 있다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다- 소아가정간호 백과]-제 2권 소아청소년 질병 안전사고 예방-B형 간염 예방접종, B형 간염 예방접종을 꼭 받아야 하는 사람, B형 간염 예방접종을 받을 때 유의할 사항,
- B형 간염을 과거에 한 번도 앓은 적이 없는 아이들과 성인들에게 B형 간염 예방접종을 주는 방법 등 참조.
Neonatal hepatitis B 신생아 B형 간염

Figure 150: During pregnancy, an intrauterine fetus is less susceptible to infection by the mother’s hepatitis B virus.
However, a mother who carries hepatitis B virus or has hepatitis B infection can cause the baby to contract hepatitis B virus from her mother during delivery, resulting in newborn hepatitis B infection. Source-Pediatric Family Medicine Encyclopedia and “Illustrations from Pregnancy in Anatomical Illustrations appear courtesy of the copyright owner c Carnation Company, Los Angeles, CA 1962”

Picture 151. A mother carrying hepatitis B virus or hepatitis B infection can cause the baby to contract hepatitis B virus from her mother during delivery, resulting in a newborn hepatitis B infection. However, it is common that the fetus in the womb during pregnancy is less susceptible to the hepatitis B virus that the mother has. Copyright ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Neonatal hepatitis in neonatal jaundice has already been described but is explained again here. In the womb, fetuses can be infected with rubella virus, cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, or herpes virus.
The viral infection can lead to fetal hepatitis.
Fetal hepatitis can lead to neonatal hepatitis after birth. During birth, the fetus from the pregnant woman can be infected with the hepatitis A virus or the hepatitis B virus, resulting in hepatitis A or hepatitis B infection in the newborn.
Symptoms or signs of such hepatitis may first appear in infancy after the neonatal period. Neonatal hepatitis can occur when a fetus or newborn is infected with pathogens such as rubella virus, cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, herpes virus, hepatitis A virus and hepatitis B virus, toxoplasma protozoa, or syphilis.
Among them, the main cause of neonatal hepatitis is hepatitis B virus.
[Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing]-Vol. 7 Pediatric and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-See Syphilis .How newborns get infected with the hepatitis B virus. When women with hepatitis B virus become pregnant, the hepatitis B virus can be transmitted to the fetus through the placenta.The hepatitis B virus may be transmitted directly to the fetus through the placenta from a pregnant woman with hepatitis B.
During delivery, the hepatitis B virus can be transmitted directly to a born baby.
A newborn baby born after birth, a newborn baby thereafter, or an infant thereafter can be infected by the mother and It can also be infected by blood transfusions. [Parents should also be at least the hal-doctors-Encyclopedia of Child and Family Nursing]-Volume 7 Child and Adolescent Infectious Diseases-See Hepatitis B.
Signs, symptoms of hepatitis b in newborns
If the fetus is infected with the mother’s hepatitis B virus around 7 to 9 months of pregnancy and the fetus gets hepatitis B, it can lead to premature delivery.
When a newborn is infected with the hepatitis B virus, the newborn can develop acute or chronic hepatitis, and in severe cases, can die from neonatal hepatitis.
Most newborns with hepatitis B can become carriers of the hepatitis B virus. Severe hepatitis B infection can delay growth and development, eating is not refreshing, stomach upset, jaundice, and yellow urine.
Diagnosis of hepatitis b in newborns
If you suspect this disease by taking the medical history, symptoms, signs, and medical examination findings together, check whether the mother carries the hepatitis B virus, is currently suffering from hepatitis B, and whether or not you have suffered from it in the past.
Hepatitis B virus antigens and antibodies are tested by blood, and, liver function test, CBC blood test, direct type bilirubin and indirect type bilirubin test are performed to confirm the presence of hepatitis B virus, antigen, antibody, liver function test in newborn blood.
Treatment of hepatitis b in newborns
Adult chronic hepatitis B is treated with antiviral drugs such as Interferon-alfa, Lamivuden, and Adefovir, but There are still no special drugs for the treatment of neonatal hepatitis. Treat according to symptoms.
If she was born to a mother who carries the hepatitis B virus, or to a mother who has hepatitis B, but the baby has not been infected with hepatitis B, she should not breastfeed her baby.
To prevent the newborn from becoming infected with the hepatitis B virus from her mother, her newborn is vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine shortly after birth and is given a hepatitis B immunoglobulin injection for preventive treatment. In this case, breastfeeding may be possible.
출처 및 참조 문헌
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
|
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP 미국 소아과 전문의, 한국 소아청소년과 전문의 이상원 저 “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다. The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.” |