신생아 배꼽 헤르니아(신생아 배꼽 탈장증/신생아 제 탈장증), Umbilical hernia of newborn infants
- 배꼽 륜(제륜)이 배꼽과 배꼽의 바로 밑에 있는 복벽에 있다.
- 이 제륜은 태어난 후 막히는 것이 정상입니다.
- 태어날 때부터 제륜이 미약하거나 불완전하게 막혀 있을 때 배꼽 피부층의 바로 밑에 구멍이 조그마해서 생길 수 있다.
- 이 구멍을 통해 복강 내에 있는 창자나 복막의 일부가 배꼽 피부층 밑까지 불쑥 밀고 나온 것을 배꼽 헤르니아, 제 탈장, 또는 배꼽 탈장이라고 한다.
- 그로 생긴 증상 징후를 배꼽 탈장증 또는 제 탈장증이라 한다.
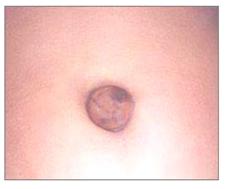
사진 100. 배꼽 탈장(배꼽 헤르니아, 제 탈장)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
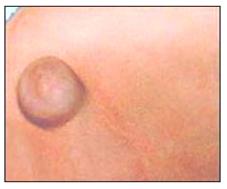
사진 101. 배꼽 탈장(배꼽 헤르니아/제 탈장)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
| 배꼽 헤르니아(배꼽 탈장증/제 탈장증)의 증상 징후 |
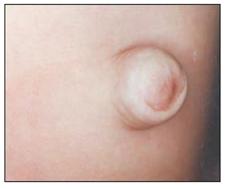
사진 102. 배꼽 탈장(배꼽 헤르니아, 제 탈장)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
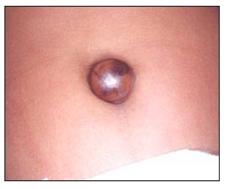
사진 103. 배꼽 탈장(배꼽 헤르니아, 제 탈장)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 배꼽 헤르니아의 크기와 모양이 다양하다.
- 길이는 1~5cm 정도이고 성인의 새끼손가락 끝 부분이나 엄지손가락 끝부분을 배꼽 헤르니아의 제륜을 통해서 복강 내로 조금 밀어 넣을 수 있다.
- 이 때 배꼽 헤르니아의 제륜의 크기가 어느 정도로 큰지 감지할 수 있다.
- 일반적으로 배꼽 헤르니아가 있는 신생아가 잘 때나 배에 힘을 많이 주지 않을 때, 즉 복강내 압력을 조금도 주지 않고 가만히 있을 때는 배꼽 헤르니아가 없는 것과 같이 보이거나 배꼽 헤르니아가 아주 작아진다.
- 그렇지만 심하게 울거나 배에 힘을 많이 줄 때는 복막의 일부나 창자의 일부가 배꼽 헤르니아의 제륜에 있는 구멍을 통과해서 배꼽 피부를 불쑥 밖으로 밀기 때문에 배꼽 헤르니아가 위로 불쑥 솟아 나오게 되고 아주 크게 보일 수 있다.
- 배꼽 피하층 속으로 불쑥 솟아 나온 배꼽 헤르니아의 내용물을 손으로 만져 보면 뽀드득 뽀드득 소리가 날 수 있다.
- 헤르니아의 내용물을 손가락 끝부분으로 복강 속으로 밀어 넣으면 내용물이 헤르니아의 제륜에 있는 헤르니아 구멍을 통과해서 복강 속으로 다시 들어가는 것을 감지할 수 있다.
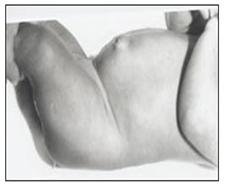
사진 104. 배꼽 탈장
(배꼽 헤르니아, 제 탈장)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
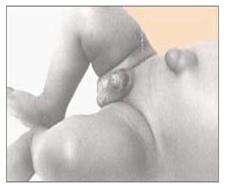
사진 105. 배꼽 탈장(배꼽 헤르니아, 제 탈장)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
| 배꼽 헤르니아(배꼽 탈장증/제 탈장증)의 치료 |
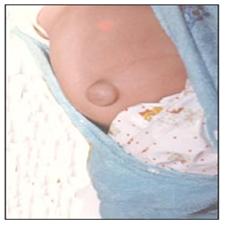
사진 106. 배꼽 탈장(배꼽 헤르니아)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
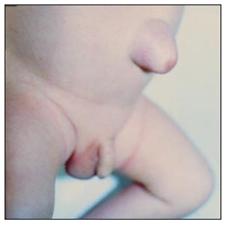
사진 107. 배꼽 탈장(배꼽 헤르니아)
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 대부분의 배꼽 헤르니아는 4~5세가 될 때까지 저절로 없어진다.
- 대개의 경우, 그대로 두고 관찰적 치료하는 것이 치료의 전부이다.
- 그렇지만 배꼽 헤르니아의 제륜이 동전 하나가 쉽게 들어갈 수 있을 정도 클 때나 장관의 일부가 헤르니아의 제륜을 통하여 배꼽 헤르니아 속으로 쉽게 빠져나올 수 있을 정도로 클 때나 복강 내 장기의 일부가 배꼽 헤르니아 속으로 빠져 나온 후 복강 속으로 다시 들어가지 않을 때는 수술로 치료해야 한다.
- 그렇지만 이런 이유로 배꼽 헤르니아를 수술로 치료하는 경우는 극히 드물다.
- 아주 큰 배꼽 헤르니아도 수술로 치료하지 않고 관찰적 치료를 하는 것이 보통이다
- 4~5세가 될 때까지 배꼽 헤르니아가 저절로 없어지지도 않고 미관상 보기에 흉하고 계속 남아 있거나 학교에서 놀림거리가 되거나 그 아이 자신이 배꼽 헤르니아 때문에 걱정을 많이 할 때는 유치원에 입학하기 바로 전에 의사와 상의하여 수술로 치료해 줄 수 있다. 그런 경우는 아주 드물다.
- 그러나 될 수 있는 한 수술로 치료하기보다 적어도 5~6세까지 저절로 없어질 때까지 꾹 참는 것이 더 좋다.
- 수술로 치료할 때 배꼽을 절대로 잘라내지 않도록 극히 주의해야 한다.
Umbilical hernia of newborn infants 신생아 배꼽 헤르니아(신생아 배꼽 탈장증/신생아 제 탈장증)
The navel ring is located on the navel and on the abdominal wall just below the navel.
It is normal for this ring to be blocked after birth.
It can be caused by a small hole just below the navel skin layer when the ring is weak or incompletely blocked from birth.
A part of the intestine or peritoneum in the abdominal cavity that comes out through this hole is called an umbilical hernia.
The resulting are called umbilical hernia .

Picture 100. Umbilical hernia (navel hernia). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 101. Umbilical hernia. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Symptoms, signs of umbilical hernia

Picture 102. Umbilical hernia (navel hernia). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 103. Umbilical hernia (navel hernia). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Navel hernias vary in size and shape.
The length is about 1~5cm, and the tip of an adult’s little finger or the tip of the thumb can be pushed a little into the abdominal cavity through the ring of the navel hernia.
At this time, it is possible to detect how large the size of the umbilical ring of the navel hernia is.
In general, newborns with umbilical hernias look like no umbilical hernia or have very small umbilical hernias when sleeping or when there is not much pressure on the stomach, that is, when there is no pressure in the abdominal cavity and remain still.
However, when crying severely or giving a lot of power to the stomach, part of the peritoneum or part of the intestine passes through the hole in the umbilical ring of the umbilical hernia and pushes the umbilical skin out of it, causing the umbilical hernia to bulge upward and may appear very large.
If you touch the contents of the navel hernia, which protrudes into the subcutaneous layer of the navel with your hand, it may make a popping sound.
When the contents of the hernia are pushed into the abdominal cavity with the tip of a finger, it can be detected that the contents pass through the hernia cavity in the annulus of the hernia and re-enter the abdominal cavity.

Picture 104.Umbilical hernia (Belly hernia) Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 105. Umbilical hernia (navel hernia). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP Treatment of umbilical hernia (belly hernia)

Picture 106. Umbilical hernia (navel hernia). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP Picture

107. Umbilical hernia (navel hernia). Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Most umbilical hernias go away on their own until they are 4-5 years old. In most cases, treatment is all about leaving it as it is and performing the observational treatment.
However, when the umbilical hernia is large enough to be easily inserted by a coin, or when a part of the intestine is large enough to easily escape into the umbilical hernia through the hernia, or after a part of the organs in the abdominal cavity has fallen into the umbilical hernia.
If it does not go back into the abdominal cavity, it must be treated with surgery. However, for this reason, umbilical hernia is rarely treated surgically.
Even very large navel hernias are usually not treated with surgery, but observational treatment. Until the age of 4-5, if the navel hernia does not go away on its own and remains unsightly and remains unsightly, becomes a joke at school, or if the child himself is worried about navel hernia, consult a doctor immediately before entering kindergarten. It can be treated with surgery.
Such cases are very rare.
However, it is better to hold on until it disappears on its own by at least 5-6 years of age, rather than treating it with surgery as much as possible.
When treating with surgery, extreme care must be taken to never cut off the belly button.
출처 및 참조 문헌
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
|
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP 미국 소아과 전문의, 한국 소아청소년과 전문의 이상원 저 “부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다. The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.” |