신생아 비후성 유문 협착증(신생아 비후성 유문 협착), Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in newborn infants
| 비후성 유문 협착증(신생아 비후성 유문 협착)의 원인 |
- 위에서 십이지장으로 이행되는 경계 부분이 유문이다.
- 유문의 벽속에 있는 근육이 비정상적으로 비대되어 유문이 아주 막히거나 거의 막히는 병을 비후성 유문 협착증이라고 한다.
- 비후성 유문 협착증으로 유문이 조금 막히거나 거의 막히는 정도에 따라 위 속에 있는 음식물이나 위액이 유문을 통과해서 십이지장관 속으로 정상적으로 내려갈 수 없거나 더 이상 내려갈 수 없다.
- 신생 여아들보다 신생 남아들에게 이 병이 더 잘 발생될 수 있다.
- 150명의 신생 남아들 중 1명, 750명의 신생 여아들 중 1명에게 이 병이 발생될 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다- 소아가정간호 백과]-제 9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환 참조.
| 비후성 유문 협착증(신생아 비후성 유문 협착)의 증상 징후 |
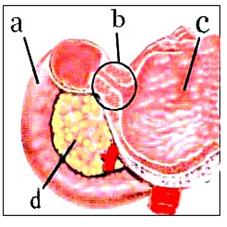
그림 204.유문 협착증
a-십이지장, b-협착된 유문, c-위, d-췌장
출처: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216,
Division of Laboratories, USA과 소아가정간호백과
- 이 병의 정도, 진행 과정, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 생후 7일 이전 이 병이 거의 생기지 않으나 생후 2~3주경 생기기 시작한다.
- 유문 벽 속에 있는 근육이 서서히 비대되기 시작하다가 나중에 위 속에 있는 내용물이 십이지장 관 속으로 더 이상 내려갈 수 없을 정도 완전히 비대되고 마지막으로는 유문이 거의 완전히 막힐 수 있다.
- 비후된 유문 벽의 정도에 따라 비후성 유문 협착증의 증상 징후가 다르게 나타난다.
- 초기에는 먹은 모유나 인공영양 등을 조금씩 울컥울컥 토하다가 이 병이 점점 더 진행되어 유문 벽 속 근육이 더 많이 비후되면서 유문이 거의 완전히 막히면 심하게 구토한다.
- 이 때 모유나 인공영양을 먹인 후 바로 분수가 솟아나는 것처럼 왈칵왈칵 구토한다.
- 아기가 모유나 인공영양을 몹시 배고픈 듯이 먹다가도 심하게 구토한다. 먹은 직후 또는 먹고 난 잠시 후 토하기도 한다.
- 구토물 속에는 먹은 엄마의 젖이나 인공영양과 점액이 섞여 있는 것이 보통이다.
- 파란 담즙은 섞여 있지 않는 것이 보통이다.
- 드물게는 소량의 피가 구토 물 속에 섞여 있을 수 있다.
- 계속 구토하고 먹지 못해 필요한 칼로리와 수분을 충분히 섭취할 수 없기 때문에 탈수가 되고 기운이 없고 몸이 축 늘어질 수 있다.
- 이런 증상 징후가 오랫동안 계속되면 성장 발육에도 지장이 생기고 몸이 마르고 힘이 하나도 없게 된다.
| 비후성 유문 협착증(신생아 비후성 유문 협착)의 진단 치료 |
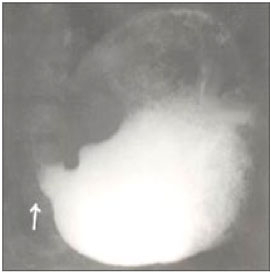
사진 205.바륨 액을 먹인 후 찍은 위 십이지장관 X선 사진. 비후성 유문 협착증으로 유문이 막혀 위 속에서 바륨이 십이지장 속으로 더 이상 내려가지 않는다. 화살표시로 가리킨 부분에 유문 협착이 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
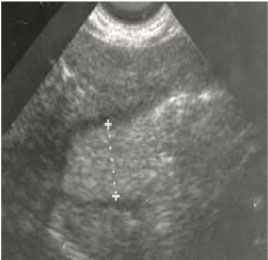
사진 206.위 십이지장 초음파 사진으로 비후성 유문협착증을 진단할 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
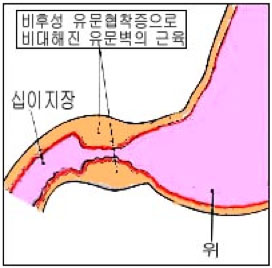
그림 207.비후성 유문협착증
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 이 병이 있으면 엄마의 젖이나 인공영양을 먹는 대로 구토하기 때문에 초기에 이 병을 감별 진단하는 데 관심가지면 쉽게 진단할 수 있다.
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 위장 초음파 사진 검사로 진단할 수 있다.
- 액체 바륨을 먹인 후 위와 십이지장 X선 사진검사로 진단할 수 있다.
- 병원에 입원해서 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 재수화 치료를 하고 현상 유지 수화치료를 하면서 전반적 건강 상태가 양호해지면 반지처럼 동그랗게 비후된 유문벽 근육을 잘라주는 수술치료로 간단히 완치될 수 있다.
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in newborn infants 신생아 비후성 유문 협착증(신생아 비후성 유문 협착)
Causes of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (neonatal hypertrophic pyloric stenosis)
- The part of the boundary that transitions from the stomach to the duodenum is the pylorus.
- Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is a disease in which the pylorus is very blocked or almost blocked due to abnormal enlargement of the muscles in the wall of the pylorus. With hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, depending on the degree to which the pylorus is slightly or almost blocked, food or gastric juice in the stomach cannot pass through the pylorus and normally descend into the duodenal tract or can no longer go down.
- New boys are more likely to develop this disease than new girls. The disease can develop in 1 in 150 new boys and 1 in 750 new girls.
- [Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Refer to Volume 9, Children’s and Adolescent Digestive Diseases. Symptoms signs of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (neonatal hypertrophic pyloric stenosis) Figure 204 Pylori stenosis a-duodenum, b-constricted pylorus, c-stomach, d-pancreas
- Source: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Department of Laboratories, USA Pediatric clinic and Family Nursing Encyclopedia Symptoms and signs differ depending on the severity of the disease, the course of the disease, and the presence or absence of complications.
- The disease rarely occurs before 7 days of age, but it starts to develop around 2-3 weeks of age.
- The muscles in the pyloric wall gradually begin to enlarge, and later the contents of the stomach become completely can no longer descend into the duodenal duct, and finally, the pylorus can be almost completely blocked.
Symptoms of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis appear differently depending on the degree of the thickened pyloric wall.
- In the beginning, they vomit little by little with breast milk or artificial nutrition, and then the disease progresses more and more, and the muscles in the pyloric wall thicken more, and when the pylorus is almost completely blocked, they vomit severely. At this time, immediately after feeding breast milk or artificial nutrition, they vomit as if a fountain springs up.
- The baby vomits violently while eating breast milk or artificial nutrition as if it were very hungry. They may vomit immediately after eating or shortly after eating.
- The vomit is usually mixed with mother’s milk or artificial nutrition and mucus.
- The blue bile is usually not mixed. Rarely, a small amount of blood may be mixed in the vomiting water.
- Your baby can’t get enough calories and fluids because your baby still vomiting and not eating, which can lead to dehydration, lack of energy.
- If these symptoms persist for a long time, growth and development will also be impaired, the body will dry out and have no strength.
Diagnostic treatment of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (neonatal hypertrophic pyloric stenosis)

- Picture 205: X-ray of the gastric duodenal tube taken after feeding the barium solution. With hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, the pylorus is blocked and barium from the stomach no longer descends into the duodenum. There is a pyloric stricture at the point indicated by the arrow. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

- Picture 206. An ultrasound picture of the gastric duodenum can diagnose hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

- Figure 207. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- If your baby has this disease, your baby will vomit as soon as your baby eats mother’s milk or artificial nutrition, so it can be easily diagnosed if you are interested in the differential diagnosis of the disease in the early stages.
- If the disease is suspected by combining the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings,
- it can be diagnosed with gastrointestinal ultrasonography.
- It can be diagnosed with an x-ray of the stomach and duodenum after feeding liquid barium.
- After hospitalization, rehydration treatment with intravenous glucose electrolyte solution and status maintenance hydration treatment can be cured simply with surgical treatment that cuts the thickened pyloric wall muscle like a ring.
출처 및 참조 문헌
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.