신생아 상완신경총 마비(신생아 상박 신경총 마비/상박 신경총, 상지마비/에르브-뒤시엔느 마비/클룸프케 마비), Brachial plexus palsy in newborn infants(Erb-Duchenne Palsy/ Klumpke Palsy)
| 신생아 상완신경총 마비의 원인 |
사진 199. 경부 척추 속에 경부 척수가 들어 있고 그 척수에서 상완신경총이 나온다. 이 상완신경총에서 여러 종류의 말초신경이 나와 팔 등에 분포된다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
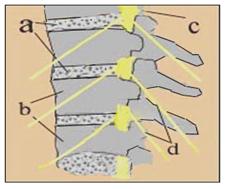
그림 200. 척수부와 말초신경
a-추간원판(디스크), b-척추, c-척수, d-척수신경
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 31쌍의 척수신경이 척수에서 기원한다.
- 즉 8쌍의 경수신경,
- 12쌍 흉수신경,
- 5쌍 온수신경,
- 5쌍 천수신경,
- 한 쌍 미부신경이 있고 그 척수 신경이 분포 전 분지가 마비될 수 있다.
- 경부 척수에서 나온 척수신경의 일부와 흉부 척수에서 나온 척수신경의 일부를 통틀어 상박 신경총, 또는 상완신경총이라고 한다.
- 상완신경총의 척수신경들의 일부 신경이 어깨·팔·손 등의 신체 부위에 분포된다.
- 난산 분만으로 태어날 때 아기의 어깨나 팔을 너무 세게 잡아당기거나 목을 한쪽으로 너무 세게 구부리거나 잡아당길 때 상완신경총의 척수신경의 일부가 손상되고 마비될 수 있다. 이렇게 생긴 상완신경총 마비를 상지마비라고 한다.
- 제 5~6 경수신경(경부 척수신경)이 마비되어 생기는 상완신경총 마비를 에르브-뒤시엔느마비(Erb-Duchenne palsy)라고 한다.
- 제 7∼8 경수(경부)척수신경과 제 1 흉수(흉부)척수신경이 마비되어 생기는 상완신경총 마비를 클룸프케(Klumpke) 마비라고 한다.
- 여러 종류의 상완신경총 마비는 상완신경총에 있는 여러 개의 척수신경 중 한 개나 혹은 그 이상 몇 개가 척추에
-
- 눌리거나
- 타박상 등으로 손상되거나
- 그 척수신경이 시작되는 척수신경 기시 부위에서 빠져 나와 눌리거나
- 끊길 때 생길 수 있다.
| 신생아 상완신경총 마비의 증상 징후 |
- 상완신경총에 속한 여러 종류의 척수신경들 중 척수신경의 어느 부분에 손상되었는지,
- 손상된 부위와 정도,
- 손상된 척수신경의 종류, 합병증의 유무, 원인, 손상의 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 제 5∼6 경수 척수신경이 마비되어 에르브-뒤시엔느 마비가 생기면 그쪽 위팔이 주로 마비되고, 그쪽 아래팔과 손에는 마비가 생기지 않는다.
- 제 7∼8 경수 척수신경과 제 1흉수 척수신경이 마비로 클룸프케 마비가 생기면 그쪽 아래팔만 마비될 수 있고 위 아래팔 모두 마비될 수 있다.
- 위 아래팔과 그쪽 손에 분포된 상완신경총이 마비되면 상완신경총이 분포된 쪽 위 아래팔과 손 근육도 마비된다.
- 따라서 마비된 쪽 팔이 축 늘어지며 그 팔을 자유롭게 움직일 수 없다.
- 한쪽 어깨에서 위팔 아래팔과 그쪽 손까지 분포되어 있는 상완신경총 전부가 마비되면 그 쪽 어깨·팔·손이 마비되어 잘 움직일 수 없다.
- 상완신경총 마비의 정도, 마비된 척수신경의 종류, 부분에 따라 마비된 쪽 손을 움직일 수가 없는 경우와 그쪽의 어깨와 팔을 조금밖에 움직일 수 없는 마비도 생길 수 있다.
- 신생아가 깜짝 놀랄 때나 무슨 이유로 양쪽 손과 팔을 양옆으로 활짝 벌렸다가 곧바로 앞으로 두 팔을 모으면서 마치 누구를 갑자기 얼싸 안는 듯한 자세를 취하는 원시 반사를 모로 반사(만세반사)라고 한다. 상완신경총 마비가 있는 신생아에게 모로 반사가 나타날 때 마비된 쪽의 팔을 몸통 밖으로 활짝 폈다가 다시 몸통의 중앙으로 가져오는 팔의 움직임이 나타날 수 없다.
- 마비가 오랫동안 지속되면 마비되어 있는 쪽 위팔이 어깨 밖으로 틀려 돌아가고, 위팔이 내전되며 팔꿈치를 펴게 된다. p.00 뇌성마비 참조.
- 클룸프케 마비로 한쪽 아래팔과 손이 마비되었을 때는 그 손을 의식적으로 움직일 수 없고 파악반사가 없어진다.
- 피부 감각도 상실될 수 있다.
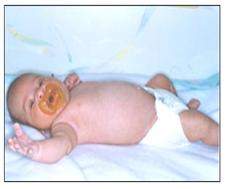
사진 201. 상완신경총 마비. 좌 상완 신경총 마비로 왼쪽 팔을 정상적으로 움직이지 못한다. 이런 경우 비대칭성 모로반사가 나타난다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
| 신생아 상완신경총 마비의 진단 |
- 난산으로 태어났거나 둔위 전진 분만으로 태어난 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견, 척추 X선 사진 등을 종합해 진단한다.
- 상완신경총 마비가 있을 때는 마비가 된 쪽의 척추와 위팔뼈(상완골) 등이 동시 골절될 수 있다.
- 척추뼈와 팔뼈 X선 사진을 찍어 척추나 팔뼈도 골절됐는지 알아보는 것도 중요하다.
| 신생아 상완신경총 마비의 치료 |
- 상완신경총의 손상의 정도와 손상 부위에 따라 다르게 치료한다.
- 척추 골절로 상완신경총의 일부의 척수신경이 잘리거나 척수신경 기시 부분이 척수에서 빠져 나와 생긴 상완신경총 마비는 완치될 가능성이 희박하다.
- 골절된 척추를 몇 주 동안 일정한 위치에 고정시켜 치료하기도 하고 마비된 팔이나 손을 수동적으로 운동시키고 마사지해서 치료한다.
- 어떤 때는 상완신경총 마비가 완전히 낫지 않고 평생 동안 마비된 상태로 남아 불구자가 되기도 한다.
- 상완신경총의 일부가 단순히 조금 눌려서 조금 손상되고 끊어지지 않았을 때는 2∼3개월 이내에 자연적으로 회복되기도 한다.
- 팔이나 손에 생긴 마비는 마사지나 다른 수동적 물리치료로 치료할 수 있다.
- 때로는 골절된 척추를 수술 치료한다.
Brachial plexus palsy in newborn infants (Erb-Duchenne Palsy/ Klumpke Palsy) 신생아 상완신경총 마비(신생아 상박 신경총 마비/상박 신경총, 상지마비/에르브-뒤시엔느 마비/클룸프케 마비)
Causes of brachial plexus paralysis in newborns

Picture 199. The cervical spinal cord is in the cervical spine, and the brachial plexus comes out of the spinal cord. From this brachial plexus, several types of peripheral nerves come out and are distributed in the arms. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Figure 200. Spinal cord and peripheral nerves.
a-intervertebral disc (disc), b-spine, c-spinal cord, d-spinal nerve Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 31 pairs of spinal nerves originate in the spinal cord.
- That is, 8 pairs of nerve nerves,
- 12 pairs of pleural nerves,
- 5 pairs of heated nerves,
- 5 pairs of pleural nerves,
- There is a pair of caudal nerves, and the branch may be paralyzed before the spinal nerve is distributed.
- The part of the spinal nerve from the cervical spinal cord and the part of the spinal nerve from the thoracic spinal cord are collectively called the brachial plexus.
- Some nerves of the spinal nerves of the brachial plexus are distributed in body parts such as shoulders, arms, and hands. Part of the spinal nerve of the brachial plexus can be damaged and paralyzed when the baby’s shoulders or arms are pulled too hard, or the neck is bent or pulled too hard to one side when born with a difficult delivery.
- Paralysis of the brachial plexus that occurs in this way is called upper limb paralysis. The paralysis of the brachial plexus caused by paralysis of the 5th to 6th nerve (cervical spinal nerve) is called Erb-Duchenne palsy.
- Paralysis of the brachial plexus caused by paralysis of the 7th to 8th carotid (neck) spinal nerves and the first pleural (thoracic) spinal nerves is called Klumpke’s paralysis.
- In several types of brachial plexus paralysis, one or more of several spinal nerves in the brachial plexus are involved in the spine.
- Pressed or Damaged by bruises, etc. The spinal nerve comes out of the origin of the spinal nerve and is pressed or It can occur when it is cut off.
Symptoms of brachial plexus paralysis in newborns
- Which part of the spinal nerve is damaged among the various types of spinal nerves belonging to the brachial plexus,
- The area and extent of the damage, Symptoms differ depending on the type of damaged spinal nerve, the presence or absence of complications, the cause, and the severity of the injury.
- When the 5th to 6th carotid spinal nerves are paralyzed and Erv-Dussien’s paralysis occurs, the upper arm is mainly paralyzed, and the lower arm and hand are not paralyzed.
- When Klumpke’s paralysis occurs due to paralysis of the 7th to 8th carotid and first pleural spinal nerves, only the lower arm may be paralyzed, and both upper and lower arms may be paralyzed.
- When the upper and lower arms and the brachial plexus distributed in the hand are paralyzed, the upper and lower arms and hand muscles on the side where the brachial plexus is distributed are also paralyzed.
- Therefore, the paralyzed arm is drooping and the arm cannot be moved freely.
- When the entire brachial plexus is distributed from one shoulder to the upper arm and the lower arm and the hand is paralyzed, the shoulder, arm, and hand of that side are paralyzed and cannot move well.
- Depending on the degree of paralysis of the brachial plexus, the type and part of the paralyzed spinal nerve, there may be cases in which the paralyzed hand cannot be moved, and the shoulder and arm of the paralyzed side cannot be moved only a little. When a newborn baby is surprised or for some reason, the primordial reflex is called the Moro Reflex,
- which takes a posture as if suddenly embracing someone with both hands and arms wide open to the side and then putting both arms straight forward.
- In newborns with brachial plexus paralysis, when the Moro reflex appears, the arm movement that brings the paralyzed arm out of the torso and then brings it back to the center of the torso cannot appear.
- If the paralysis persists for a long time, the upper arm on the paralyzed side twists out of the shoulder and turns, and the upper arm is adducted and the elbow is stretched. See Cerebral Palsy.
- When one forearm and hand are paralyzed due to Klumpke’s paralysis, the hand cannot consciously move and the grasping reflex disappears. Skin sensation can also be lost.

Picture 201. Paralysis of the brachial plexus. Left brachial plexus paralysis prevents normal left arm movement. In this case, asymmetric Moro reflection appears. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Diagnosis of brachial plexus paralysis in newborns
- The diagnosis is made by taking the medical history, symptoms, signs, examination findings, and spinal X-ray pictures, etc., which were born with difficulty in birth or were born with a blunt forward delivery.
- When the brachial plexus is paralyzed, the vertebrae and the upper arm bone (humerus) of the paralyzed side can be fractured at the same time.
- It is also important to take X-rays of the vertebrae and arm bones to see if the spine or arm bones are also fractured.
Treatment of neonatal brachial plexus palsy
- Treatment differs depending on the degree of damage to the brachial plexus and the site of the injury.
- Brachial plexus paralysis, which is caused by a spinal nerve breakage of a part of the brachial plexus due to a vertebral fracture, or the origin of the spinal nerve, is pulled out of the spinal cord, is unlikely to be cured.
- The fractured spine is fixed in a certain position for several weeks to treat, and the paralyzed arm or hand is passively exercised and massaged.
- Sometimes brachial plexus paralysis is not completely healed and remains paralyzed for the rest of life, resulting in a disabled person.
- When a part of the brachial plexus is damaged a little by simply pressing a little, and it is not broken, it recovers naturally within 2 to 3 months.
- Paralysis in the arm or hand can be treated with massage or other passive physical therapy. Sometimes, a fractured spine is surgically treated.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.