잠재고환(잠복고환/정류고환), Cryptorchidism (Undescended testis)
| 잠재고환(잠복고환/정류고환)의 원인 |
- 대부분의 경우, 적어도 임신 32주 되기 전 까지 남 태아의 고환이 뱃속(복강 내)에서 양쪽의 서혜관을 통과하여 양쪽 음낭 속으로 내려오는 것이 정상이다.
- 출생 시 체중이 450~910g 되는 대부분의 남 미숙 신생아들의 고환이 음낭 속에 들어 있지 않고, 출생 시 체중이 2,041~2,490g 되는 남 미숙 신생아들의 17%는 태어난 직후 고환이 음낭 속에 들어 있지 않다.
- 만삭에 출생한 신생 남아들의 3~4%에서 고환이 음낭 속에 들어 있지 않다.
- 출생 후 한쪽 또는 양쪽 고환이 음낭 속에 완전히 내려와 있지 않고 복강 내 그대로 남아 있거나, 복강 밖으로 나와 있지만 음낭 속에까지 완전히 내려와 있지 않고 그 쪽 복벽의 바로 바깥 서혜관 속에 있다.
- 이러한 고환을 잠재 고환, 잠복 고환 또는 정류 고환이라고 한다.
- 이소성 고환도 잠재 고환에 속한다.
- 고환이 음낭 속에 있지 않고 때로는 전위되어 있는 경우도 있다.
- 이런 고환을 전위 고환이라고 한다.
| 잠재고환(잠복고환/정류고환)의 증상 징후 |
- 한쪽 고환이 음낭 속으로 내려와 있고 다른 쪽 고환은 복강 내나 그 쪽 복벽의 바로 바깥에 있는 서혜관 속에 있을 수 있다.
- 양쪽 고환이 음낭 속으로 내려와 있지 않을 수 있다.
- 만삭에 태어난 남 신생아들의 3∼4%, 아주 작은 미숙 신생 남아들의 고환이 음낭 속으로 내려와 있지 않을 때가 더 많다.
- 이와 같이 한쪽 또는 양쪽 고환이 음낭 속에 내려와 있지 않은 상태에서 태어났을 때, 한쪽 또는 양쪽 고환이 음낭 속으로 완전히 내려와 있지 않고 뱃속에 그대로 남아 있거나 서혜관 속에 남아 있을 수 있다.
- 서혜관 속에 있던 잠재 고환이 생 후 2~ 3개월까지 음낭 속으로 내려오는 경우도 많다.
- 태어났을 때는 복강 내에 있던 잠재 고환이 출생 후 복강 속에서부터 복강 속 바로 바깥 서혜관 속 쪽으로 점점 이동하여 음낭 속 쪽을 향해 계속 내려오는 중 더 이상 내려오지 않고 복강 속이나 서혜관 속에 그대로 머물러 있을 수 있다.
- 태어날 때 복강 속이나 서혜관 속에 있던 잠재 고환이 적어도 첫 돌 까지 음낭 속으로 서서히 내려오는 경우도 있다.
- 그러나 첫 돌이 될 때까지 잠재 고환이 음낭 속으로 완전히 내려오지 않으면, 음낭 속으로 완전히 내려올 가능성은 아주 희박하다.
- 2~3세까지 잠재 고환이 복강 내에 그대로 남아 있으면, 잠재 고환의 기능이 점차로 쇠퇴되기 시작하는 것이 보통이다.
- 그 후에 잠재 고환을 복강 내에서 복강 밖으로 꺼내 음낭 속으로 넣는 수술 치료를 해도, 고환은 정자 생성 기능을 정상적으로 할 수 없다.
- 또 복강 속에 있는 대부분의 잠재 고환은 복강 밖에 있는 정상 고환 크기보다 더 작고, 복강 속에 오랫동안 있는 잠재 고환이나 쇠퇴된 잔여 잠재 고환에 악성 종양이 생길 수 있다.
- 고환이 음낭 속에서 발견되지 않으면 부모다 많이 걱정한다. 그 아들이 5~6세 되면 그 아이 자신도 걱정하는 것이 보통이다.
- 잠재 고환이 있는 쪽 서혜부 속에 서혜부 탈장이 함께 생길 수 있다.
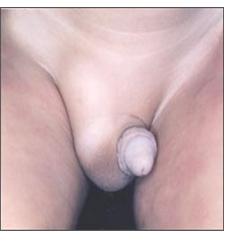
사진 2-17. 왼쪽 잠재 고환.
왼쪽 고환이 음낭 속으로 내려와 있지 않다. 그리고 오른쪽에 서혜부 허니아가 있다(서혜부 탈장).
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
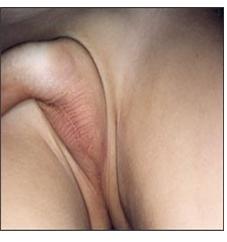
사진 2-18. 양쪽의 잠재 고환.
양쪽 고환이 음낭 속으로 내려와 있지 않다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
| 잠재고환(잠복고환/정류고환)의 진단 |
- 병력·증상 징후·진찰소견을 종합해서 이 병을 진단한다.
- 고환이 음낭 속에 있는지 알아보기 위해 손으로 검진하기 전 음낭을 육안으로 잘 살펴보면, 고환이 없는 쪽 음낭은 잘 발달되어 있지 않고 음낭 피부 주름살도 적다.
- 음낭이나 서혜관 부위를 손으로 살짝 만지거나 사타구니 부위를 살짝 건드리면, 음낭 속에 있던 고환이 서혜관 속 쪽으로나 복벽의 바깥 부위 속으로 올라갔다가 음낭 속으로 다시 내려오기도 한다. 이런 고환을 퇴축성 고환(Retractile testis)이라고 한다.
- 음낭 속에 있던 퇴축성 고환이 서혜관 속이나 그 쪽의 복벽 바깥 부위 속으로 올라가 있을 때에는 음낭 속에서 고환을 정상적으로 잠시 동안 만져볼 수 없고, 고환이 음낭 속으로 다시 내려올 때에는 음낭 속에서 고환을 만져볼 수 있다.
- 이때 고환이 서혜부와 음낭 사이에 있는 서혜관 속 통로 속을 따라 올라갔다 내려왔다 한다.
- 음낭에서 서혜관 부위까지 서혜관 속 통로를 따라 따뜻한 손으로 만져보면, 서혜관 통로 속 한 부위에 숨어 있는 고환을 찾아낼 수 있다.
- 복강 내에 있는 잠재 고환이 서혜관 속이나 음낭 속으로 내려오지 않을 때에는, 복강 속 초음파 검사로 잠재 고환을 찾아낼 수 있다.
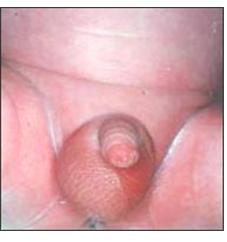
사진 2-19.왼쪽 고환이 왼쪽 음낭 속에 내려와 있지 않은 선천성 잠재고환.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
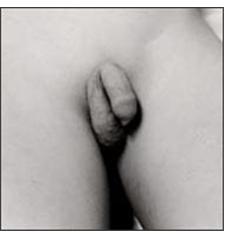
사진 2-20. 사춘기 남아의 왼쪽 잠재고환.
한쪽 고환이 없어 정서적인 문제가 생기 면 인공 고환을 음낭 속에 넣는 치료를 할 수 있다.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
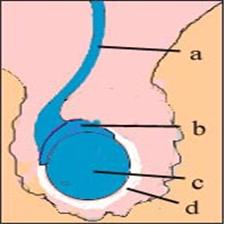
그림 2-21.고환
a-정관, b-부고환, c-고환, d-고환 초막.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
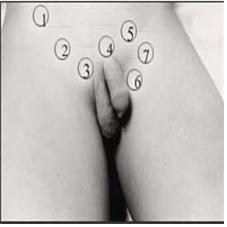
사진 2-22. 고환이 음낭 속에서 만져지지 않을 때, 고환이 선천적으로나 후천적으로 체 내외에 형성되지 않았거나, 다음과 같은 신체 부위에 있을 수 있다.
① 복강 내, ② 서혜 복부, ③ 음낭 바로 위 서혜관, ④음경 뿌리 부위, ⑤ 서혜부의 피부 바로 아래 부위, ⑥ 대퇴 서혜부위, 또는 ⑦ 복강벽 15.
Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
| 잠재고환(잠복고환/정류고환)의 감별 진단 |
- 단순 잠재 고환과 무고환증을 감별 진단하고, 남성화 선천성 부신 과다형성증(신생 여아의 경우), 생식선 자극 호르몬 결핍증, 갑상선 기능 저하증, 염색체 이상 증후군, 클라인 펠터 증후군 등이 있을 때의 고환과 단순 잠재 고환을 감별 진단해야 한다.
| 잠재고환(잠복고환/정류고환)의 치료 |
- 복강 내 잠재 고환은 생후 6~12개월부터 쇠퇴하기 시작한다.
- 그러나 복강 내 잠재고환을 전자 현미경으로 검사해보면 생후 1~2개월부터 복강 내 잠재 고환은 형태학적으로 변화되기 시작한다.
- 보통 현미경으로 검사해보면 복강 내에 남아 있는 잠재 고환은 생후 2~3세 이후부터 자연적으로 쇠퇴하기 시작한다.
- 임상적으로 생후 5~7세에 거의 완전히 쇠퇴한다.
- 미국 소아청소년과 학회에서는 적어도 생후 12개월 또는 12개월 전후에 잠재 고환을 고환 고정술로 치료하는 것을 권장한다(출처: Consultant for pediatricians, February 2009. p.50).
- 일반적으로, 생후 1세까지 잠재 고환이 음낭 속으로 자연히 내려오지 않으면, 선택적 고환 고정술 치료를 권장한다.
- 고환을 음낭 속에 넣는 수술 대신 생후 1~5주부터 HCG(Human chorionic gonadotropin) 호르몬 100~4000 IU를 매주 주사 치료한다. HCG의 총 치료 량은 10,000 IU 이다(출처: Cosultant for pediatricians, February 2009. p.50).
- 또 호르몬을 비강에 뿌려 치료하면, 복강 내 잠재 고환이 음낭 쪽으로 내려올 수 있다.
- 복강 내 있는 잠재고환을 음낭 속으로 수술로 끌어다 넣는 고환 고정술 수술 치료를 하기 전에, 생식선 자극 호르몬 방출 호르몬(Gonadotropin releasing hormone) 치료를 해볼 수 있다.
- 유럽에서는 생식선 자극 호르몬 방출 호르몬 1.0~1.2mg을 4주간 치료하면 5~20%의 치료 효과를 보지만, 요즘까지, 미국에서는 이런 치료를 하지 않고 있다.
- 잠재 고환을 가진 아이들의 일부에게는 다른 종류의 선천성 기형이 비뇨기계통에 있을 가능성이 조금 더 많고, 다른 건강 문제가 있을 때도 있다.
- 따라서 잠재 고환이 있을 때에는, 비뇨생식기 계통과 신체의 다른 계통의 어떤 부위에 어떤 종류의 선천성 기형이 있는지 알아보아야 한다.
- 복강 내 잠재 고환이 쇠퇴하여 고환 기능을 조금도 하지 못해도 쇠퇴된 복강 내 잠재 고환을 수술로 제거 치료한다.
Cryptorchidism (Undescended testis) 잠재고환(잠복고환/정류고환)
- In most cases, it is normal for the testicles of a male fetus to pass through both inguinal duct(canal)s from the stomach (in the abdominal cavity) and descend into both scrotums until at least 32 weeks of gestation.
- The testicles of most immature male newborns weighing 450-910g at birth are not contained in the scrotum, and 17% of immature male newborns weighing 2,041-2,490g at birth do not have the testicles in the scrotum immediately after birth.
- In 3 to 4% of newborn boys born at full term, the testicles are not contained in the scrotum.
- After birth, one or both testicles do not come down completely into the scrotum and remain in the abdominal cavity, or come out of the abdominal cavity, but are not completely down into the scrotum and are in the groin tube just outside of the abdominal wall.
- These tests are called undescended testes, The ectopic testis also belongs to the latent testicle.
- The testicles are not in the scrotum and are sometimes displaced.
- These tests are called avant-garde testicles.
Symptoms, Signs of Undescended testis
- One testicle may descend into the scrotum and the other testicle may be in the groin canal, either in the lower abdominal cavity or just outside the abdominal wall on that side.
- Both testicles may not descend into the scrotum. 3-4% of male newborns born at full term, and the testicles of very small immature newborn boys are more often not descending into the scrotum.
- In this way, when one or both testicles are born in a state in which one or both testicles are not descended into the scrotum, one or both testicles may remain in the abdominal cavity or in the inguinal canal without completely descending into the scrotum.
- In many cases, the Undescended testis in the inguinal canal come down into the scrotum until 2-3 months after birth.
- At birth, the Undescended testis in the abdominal cavity may gradually move from the abdominal cavity to the outside of the abdominal cavity and continue descending toward the scrotum, but remain in the abdominal cavity or in the groin.
- Potential testicles that were in the abdominal cavity or in the groin at birth may slowly descend into the scrotum at least until the first birth day.
- However, if the Undescended testis has not completely descended into the scrotum by the first stone, it is very unlikely that it will completely descend into the scrotum.
- If the undescended testis remains in the abdominal cavity by the age of 2-3, it is common for the function of the latent testicle to gradually begin to decline.
- After that, even if the latent testicle is removed from the abdominal cavity and put into the scrotum, the testicle cannot function normally for sperm generation.
- In addition, most of the undescended testis in the abdominal cavity are smaller than the size of the normal testes outside the abdominal cavity, and malignant tumors can develop in the undescended testis that has been in the abdominal cavity for a long time or the remaining latent testes that have been deteriorated.
- If the testicles are not found in the scrotum, both parents worry a lot. When the son is 5-6 years old, it is common for the child to worry about himself.
- A groin hernia may develop in the groin area on the side of the latent testicle.

- Photo 2-17. Left undescended testis. The left testicle does not descend into the scrotum. And on the right is the inguinal honey (groin hernia). Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

- Photo 2-18. undescended testis on both sides. Both testicles do not descend into the scrotum. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Diagnosis of undescended testis
- The disease is diagnosed by combining the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings.
- If you look closely at the scrotum beforehand examination to see if the testicle is in the scrotum, the scrotum on the side without the testicles is not well developed and the scrotum skin wrinkles are few.
- If you touch the scrotum or groin area with your hand or lightly touch the groin area, the testicles in the scrotum may rise into the groin tube(inguinal canal) or into the outer part of the abdominal wall and then come down into the scrotum again.
- These tests are called retractile testis.
- When the staining testicles in the scrotum are in the groin tube or outside the abdominal wall on the side, you cannot normally touch the testicles in the scrotum for a while, and when the testicles descend back into the scrotum, you can touch the testes in the scrotum. have.
- At this time, the testicles go up and down along the passage in the groin tube between the groin and scrotum.
- If you touch it with warm hands along the passage in the groin duct from the scrotum to the groin duct part, you can find the testicles hidden in one part of the groin passage.
- When the undescended testis in the abdominal cavity do not descend into the groin or scrotum, and intra-abdominal ultrasound can detect the latent testes.

Picture 2-19: Congenital undescended testis with the left testicle not descending into the left scrotum. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-20. Left undescended testisof an adolescent boy. If you have an emotional problem because you don’t have one testicle, you can put an artificial testicle into the scrotum. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 2-21. Testicles a-vas deferens. b-epididymis, c-testis, d-testis hut. Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 2-22. When the testicles are not touched in the scrotum, the testicles may not be congenital or acquired internally or externally, or maybe in the following parts of the body:
① In the abdominal cavity,
② the groin abdomen,
③ the groin (inguinal canal) just above the scrotum,
④ the penis root,
⑤ the groin skin,
⑥ the femoral groin, or
⑦ the abdominal wall
15. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Differential diagnosis of the undescended testis
- Differential diagnosis of simple undescended testis and no testis. Testicles should be diagnosed differently.
Treatment of undescended testis
- undescended testis in the abdominal cavity begins to descend from 6 to 12 months of age. However, when examining the undescended testis in the abdominal cavity with an electron microscope, the undescended testis in the abdominal cavity begin to change morphologically from 1 to 2 months of age.
- Usually, when examined under a microscope, the undescended testis remaining in the abdominal cavity begins to descend naturally from the age of 2 to 3 years of age.
- Clinically, it descends almost completely at 5-7 years of age.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics and Adolescents recommends treatment of undescended testis with testicular fixation at least around 12 or 12 months of age (Source: Consultant for pediatricians, February 2009. p. 50).
- In general, if the undescended testis does not naturally descend into the scrotum by the age of 1 year, selective testicular fixation treatment is recommended. Instead of surgery to put the testicle into the scrotum, from 1-5 weeks of age, 100-4000 IU of the hormone HCG (Human chorionic gonadotropin) is injected every week.
- The total therapeutic dose of HCG is 10,000 IU (Source: Consultant for pediatricians, February 2009. p. 50). Also, if hormones are sprayed into the nasal cavity and treated, the undescended testis in the abdominal cavity can descend toward the scrotum.
- Before performing a testicular fixation surgery in which the undescended testis in the abdominal cavity is surgically pulled into the scrotum, gonadotropin-releasing hormone treatment can be performed.
- In Europe, treatment with 1.0 to 1.2 mg of gonadotropin-releasing hormone for 4 weeks results in a treatment effect of 5 to 20%, but until now, such treatment is not performed in the United States.
- Some of the children with undescended testis are slightly more likely to have other types of congenital anomalies in the urinary system and sometimes have other health problems. Therefore, in the presence of undescended testis, it is necessary to find out what kind of congenital anomalies are present in the genitourinary system and in other parts of the body.
- Even if the undescended testis in the abdominal cavity are losing function and the testicles cannot function at all, the weakened undescended testis in the abdominal cavity is surgically removed and treated.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.