1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부에게 태어난 신생아와 적혈구 과다증, 저혈당, 저 혈당증, 췌장 랑그한스 세포기능 항진, 저 칼슘혈증, 저 마그네슘혈증, 폐 계명활성제 결핍, 특발성 흡곤란 증후군, 유리질막증, Newborn infants born to the mother with type 1 diabetis mellitus-polycythemia, hypoglycemia, pancreatic Langhans cell dysfunction, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, surfactants deficiency, idiopathic respirartory disease
- 임신부들이 임신 중 분만 전 임신 건강관리를 잘 받지 않거나
- 특히 임신 중 1형 당뇨병이 잘 치료되지 않았을 때 태아가 자연 유산되거나, 사아(死兒)로 분만되기도 하고, 1형 당뇨병을 앓는 임신부의 태아들에게 선천성 기형이 생길 확률이 1형 당뇨병이 없는 건강한 임신부의 태아들에 비해 한결 더 높다.
- 태어난 이후 1형 당뇨병을 앓는 임신부들에게 태어난 신생아들에게 여러 종류의 건강문제가 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 과거 30년 동안 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부들의 임신, 분만, 태아, 신생아의 건강관리를 더 효과적으로 잘 해서 최근 1형 당뇨병이 없는 임신부들의 임신, 분만과 거의 동등하게 임신 분만을 건강하게 할 수 있다.
- 임신 중 1형 당뇨병 관련 건강문제를 적절히 효과적으로 대처하고 치료해 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부들에게 태어난 신생아들에게 생길 수 있는 신생아 건강문제를 태어난 즉시 적절히 잘 치료 해 줄 수 있게 됐다.
- 그러나 아직도 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부에게 태어난 신생아에게 다음과 같은 건강문제들이 생길 수 있다.
- 그러므로 태어난 후 신생아는 물론 태어나기 전부터 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부의 태아들을 특별히 건강관리를 잘 해야 한다.
- 부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다- 소아가정간호백과]-제 4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유-1형 당뇨병을 앓는 엄마와 모유수유.
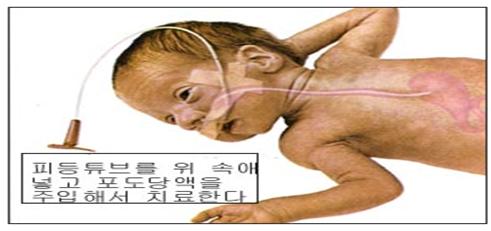
그림 213.신생아 저 혈당증을 경구용 포도당액을 입으로 먹여 치료할 수 있다. 또 비위 피딩튜브(영양튜브)를 통해 공급할 수 있고 정맥용 포도당액을 정맥주사로 주어 치료할 수 있다.

그림 215.1형 당뇨병이 있는 소아청소년들의 경우 혈당이 만들어지고 쓰이고 저장되는 과정
출처-Eli Lilly and Co. indianaspolis, Indiana과 소아가정간호백과
| 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부에게 태어난 신생아들에게 다음과 같은 건강문제들이 생길 수 있다. 태어나기 전 태아들의 건강관리를 특별히 잘해야 한다. |
- 과체중 신생아 또는 거 체구 신생아로 태어날 수 있다.
- 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부들의 태아들의 혈당 농도가 정상 이상으로 높고 혈 중 인슐린 농도가 정상 이상으로 더 높아 1형 당뇨병이 없는 임신부로부터 태어난 신생아들의 체중보다 더 크게 태어나고, 또 거 체구 신생아로 태어나는 것이 보통이다. 그래서 자연 분만하는 데도 문제가 생길 수 있다.
- 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부들의 태아의 혈당이 정상 이상으로 더 높기 때문에 출생할 때까지 그 높은 혈당 농도에 반응해서 태아들의 췌장은 인슐린을 더 많이 분비한다.
- 출생 후 바로 얼마 동안 임신 중 1형 당뇨병이 있는 분만부로부터 태어난 신생아들의 췌장 랑그한스 세포에서 인슐린이 정상 이상으로 더 많이 분비된다.
- 출생 이후 신생아의 혈당의 농도가 정상 이상으로 높지 않은데도 태어난 후 얼마 동안 인슐린이 정상 이상으로 더 많이 계속 분비되기 때문에 1형 당뇨병이 있던 임신부로부터 갓 태어난 신생아들에게 저혈당이나 저 혈당증이 심하게 생길 수 있다.
- 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부의 태아에게 과 혈당증과 과 인슐린혈증이 생길 수 있고 그로 인해 태아에게 과 산소 소모증이 생길 수 있다.
- 결과적으로 태아의 적혈구의 수가 증가되고 적혈구 과다증이 생길 수 있다.
- 신생아의 헤모글로빈 농도가 20g/dl 이상이면 적혈구 과다증으로 진단할 수 있다.
- 태아 과혈당과 과 태아 인슐린혈증으로 심장근육 이상과 심실 중격 비대증이 일시적으로 생길 수 있다.
- 저 칼슘혈증과 저 마그네슘혈증이 생길 수 있다.
- 특히 호흡곤란이 있거나 신생아에게 가사가 있으면 더 그럴 수 있다.
- 신생아의 마그네슘 혈중 농도가 1.5mg/dl 이하면 신생아 저 마그네슘 혈증이라고 진단할 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다- 소아가정간호백과]-제 5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방 참조.
- 폐 계명활성제 결핍으로 인해 폐포 표면 장력이 감소되어 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군(유리질막증)이 생기기 쉽고
- 신생아의 폐에 체액이 비정상적으로 차서 일시적 신생아 빈호흡증이 생길 수 있다. p.00 일시적 빈호흡증 참조
- 적혈구 과다증, 비효과적인 적혈구 생성, 간 기능 미숙 등으로 인해 과 빌리루빈증이 생겨 신생아 황달이 생기기 쉽다. p.00 신생아 황달 참조
- 분만 시 가사나 산소부족, 고혈당이나 저혈당, 전해질 불균형, 적혈구 과다증, 출생 시 생긴 외상, 거 체구증 등으로 중추 신경장애가 생기기 쉽다.
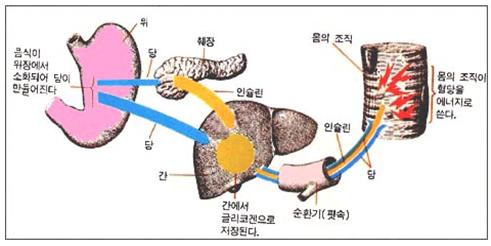
그림214.1형 당뇨병이 없는 소아청소년들의 경우 혈당이 만들어지고 쓰이고 저장되는 과정
출처-Eli Lilly and Co. Indianaspolis, Indiana과 소아가정간호백과
| 1형 당뇨병이 있는 여성이 임신이 되면 다음과 같은 검사를 해서 태아의 건강관리를 임신 중 특별히 하고 태어난 신생아를 다음과 같이 특별히 치료한다. |
- 태아의 크기를 알아보고 선천성 기형이 있나 알아보기 위해 태아 초음파 검사를 적절한 임신 중 한다.
- 임신부의 헤모글로빈 A1c를 측정한다.
- 신생아 혈당을 생후 0, 5, 1, 1.5, 2, 4, 8, 24, 36, 48시에 측정하고 그 결과 따라 치료한다.
- 혈 중 칼슘 농도를 생후 6, 24, 48시에 측정하고 그 결과에 따라 치료한다.
- 마그네슘 혈중 농도를 측정한다. 그 농도에 따라 치료한다.
- 헤모글로빈과 헤마토크리트를 생후 4, 24시에 측정한다.
- 황달이 생기나 조심히 관찰하고 필요에 따라 빌리루빈 농도를 측정한다.
- 혈 중 페리틴 농도를 생후 24시간에 측정한다.
- 그 외 통상적 신생아 건강관리를 더 조심히 해 준다.
Newborn infants born to a pregnant woman with type 1 diabetes and hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, pancreatic Langhans hyperactivity, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, pulmonary activation deficiency, idiopathic sleep disorder syndrome, vitreous membrane syndrome 1형 당뇨병이 있는 임신부에게 태어난 신생아와 적혈구 과다증, 저혈당, 저 혈당증, 췌장 랑그한스 세포기능 항진, 저 칼슘혈증, 저 마그네슘혈증, 폐 계명활성제 결핍, 특발성 흡곤란 증후군, 유리질막증
- Newborn infants born to the mother with type 1 diabetes mellitus-polycythemia, hypoglycemia, pancreatic Langhans cell dysfunction, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, surfactants deficiency, idiopathic respiratory disease
- Pregnant women do not receive good pregnancy health care before delivery during pregnancy or Particularly when type 1 diabetes is not well treated during pregnancy, the fetus is naturally aborted or delivered as a dead child, and the probability of congenital malformations in the fetuses of pregnant women with type 1 diabetes is healthy without type 1 diabetes. It is much higher than the fetuses of pregnant women.
- Newborns born to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes after birth can have many types of health problems.
- For the past 30 years, pregnant women with type 1 diabetes can better manage their pregnancy, delivery, fetus, and newborn health more effectively, making pregnancy and childbirth almost equal to those of recent pregnancy and delivery of pregnant women without type 1 diabetes.
- By properly coping with and treating health problems related to type 1 diabetes during pregnancy, it is now possible to properly treat newborn health problems that can occur in newborns born to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes, as soon as they are born.
- However, the following health problems can occur in newborns born to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes. Therefore, it is necessary to take special health care for newborns after birth, as well as for pregnant women with type 1 diabetes before birth.
- Parents should also be at least the half-doctors-Child and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 4 Breastfeeding, breastfeeding, breastfeeding with a mother suffering from type 1 diabetes.

Figure 213: Neonate hypoglycemia can be treated by oral glucose solution. In addition, it can be supplied through a nasogastric feeding tube (nutrition tube), and it can be treated by giving an intravenous glucose solution for intravenous use.

Figure 215 The process by which blood sugar is made, used and stored in children and adolescents with type 5.1 diabetes.Source-Eli Lilly and Co. Indianapolis, Indiana Department of Pediatric Home Nursing
- Newborns born to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes can have the following health problems: Before birth, you need to take special care of your baby’s health.
- It can be born as an overweight newborn or an overweight newborn.
- Pregnant women with type 1 diabetes have higher blood sugar levels than normal and their blood insulin levels are higher than normal. is average.
- That’s why natural delivery can also cause problems.
- Because the fetus’s blood sugar is higher than normal in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes, the pancreas of the fetus secretes more insulin in response to the high blood sugar levels until birth.
- Shortly after birth, the pancreatic Langhans cells of newborn babies born to delivery mothers with type 1 diabetes during pregnancy produce more insulin than normal.
- Since the newborn’s blood sugar level is not higher than normal after birth, more insulin is continuously secreted above normal for some time after birth, so hypoglycemia may be severe in newborns born from a pregnant woman with type 1 diabetes.
- Pregnant women with type 1 diabetes can develop hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia in the fetus, which can lead to hyperoxia in the fetus.
- As a result, the number of red blood cells in the fetus is increased, and an excess of red blood cells can occur. If the newborn’s hemoglobin concentration is more than 20g/dl, it can be diagnosed as red blood cell hyperplasia.
- Fetal hyperglycemia and fetal insulinemia can cause transient cardiac muscle abnormalities and ventricular septal hypertrophy.
- Hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia can occur. This can be especially true if you have trouble breathing or if your newborn has housekeeping.
- If the neonatal magnesium blood concentration is less than 1.5mg/dl, it can be diagnosed as neonatal hypomagnesemia.
- Visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 5 See artificial nutrition, milk, baby food, vitamins, minerals, protein, carbohydrates, and fat.
- Due to the deficiency of pulmonary activation agent, the alveolar surface tension is reduced, which is more prone to idiopathic dyspnea.
- Abnormal fluid filling in the newborn’s lungs can lead to transient neonatal tachypnea. See Temporary Tachypnea Hyperbilirubinosis occurs due to excessive red blood cell hyperplasia, ineffective red blood cell production, and immature liver function, and jaundice in newborns is likely to occur. See Neonatal Jaundice Central nervous disorders are easy to occur due to housework, lack of oxygen, high or hypoglycemic, electrolyte imbalance, excessive red blood cells, trauma at birth, and megacytosis during delivery.

Figure 214.1 The process by which blood sugar is made, used, and stored in children and adolescents without type diabetes Source-Eli Lilly and Co. Indianaspolis, Indiana Department of Pediatric Home Nursing.
When a woman with type 1 diabetes becomes pregnant, the following tests are performed to take special care of the fetus during pregnancy, and the newborn is specially treated as follows.
Prenatal ultrasonography is performed during pregnancy to determine the size of the fetus and to see if there are any congenital malformations.
Hemoglobin A1c in pregnant women is measured.
Newborn blood glucose is measured at 0, 5, 1, 1.5, 2, 4, 8, 24, 36, 48 hours after birth and treated according to the result.
Blood calcium concentration is measured at 6, 24, and 48 hours after birth and treated according to the results.
Magnesium blood levels are measured.
Treat it according to its concentration.
Hemoglobin and hematocrit are measured at 4 and 24 hours after birth.
If jaundice occurs, watch carefully and measure the bilirubin concentration if necessary. Blood ferritin concentration is measured at 24 hours after birth.
In addition, the usual newborn health care is more careful.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.