신생아 질식(신생아 가사), Neonatal asphyxia
- 분만 전, 분만 중, 분만 직후, 또는 그 이후 태아나 신생아가 무슨 원인으로든 산소를 충분히 공급받지 못할 때 생기는 병을 신생아 질식, 또는 신생아 가사라고 한다.
- 신생아가 심하게 질식될 때 질식의 정도에 따라 뇌, 심장, 폐, 위장, 신장 등 인간 생명 기본 유지에 꼭 필요로 하는 중요한 기관이 일시적으로, 또는 영구적으로 손상될 수 있다.
- 신생아 질식의 원인은 여러 가지가 있다.
- 여기서 출산 전 원인과 출산 후 원인으로 크게 분류할 수 있다(뇌성마비 참조).
1. 출산 전 원인
① 전신 마취를 받으면서 분만할 때 분만부가 산소 공급을 충분히 받지 못할 때
태아도 산소를 충분히 공급받지 못해 질식될 수 있다.
② 심한 심장병을 앓는 분만부에게 태어난 아기
③ 척수 마취를 받으면서 분만하는 동안 분만부의 혈압이 비정상적으로 갑자기
떨어질 때
④ 자궁 속 태아에게 피를 공급하는 분만부의 골반 강 내 동맥이 자궁으로 꼭 눌려
모체의 피가 태아에게 충분히 공급되지 않고 그로 인해 태아에게 산소 공급이
충분치 않을 때.
⑤ 빨리 분만할 수 있게 사용한 자궁 수축제로 분만부의 피가 태아에게 충분히
공급되지 못할 때.
⑥ 탯줄에 매듭이 생겨 태반에서 태아에게 피가 충분히 공급되지 않을 때
⑦ 그 외 원인으로
2. 출산 후 원인
- 신생아의 핏속에 있는 적혈구가 심하게 용혈되거나 심한 내출혈이나 외출혈로 갓 태어난 신생아에게 빈혈이 심하게 생길 때
- 갓 태어난 신생아에게 패혈증이나 뇌막염 등의 감염병으로 쇼크상태에 빠지든지,
- 심한 빈혈이 생길 때,
- 두개강 내 출혈이 생겼을 때
- 뇌 손상이 생기거나 중추신경 기능에 해가 되는 약물치료를 받은 후 숨을 제대로 쉬지 못할 때
- 심한 선천성 심장병으로 산소 결핍증이 생길 때
- 갓 태어난 신생아가 양수, 태변, 모체의 대변 등을 기도 속으로 흡입하여 기도 속이 막힐 때
- 그외 원인으로
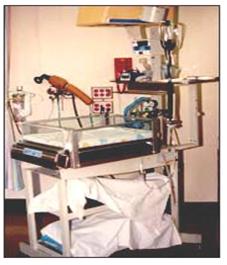
사진 208. 신생아 질식을 예방하고 질식 됐을 때 간편하게 치료에 쓸 수 있는 의료기구 및 산소 그리고 진보적 심폐소생술을 할 수 있는 약물·산소·분만 시 이런 기구들이 항시 준비되어 있어야 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
| 신생아 질식의 증상 징후 |
- 신생아 질식은 비교적 흔히 볼 수 있는 병이다.
- 질식의 원인, 정도, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 분만 전이나 분만 중 태아가 모체로부터 피를 충분히 공급받지 못해 태아의 몸속에 산소 농도가 비정상적으로 낮을 때 태아가 질식될 수 있다.
- 자궁 속에서 심하게 질식된 태아는 양수 속에 태변을 눌 수 있다.
- 태아의 심장박동이 비정상적으로 빠르거나 늦어질 수 있고, 불규칙할 수 있다.
- 때로는 태아가 자궁 내에서 사망할 수 있다.
- 출산 직후 신생아나 그 이후 신생아가 산소의 공급을 충분히 받지 못할 때도 질식될 수 있다.
- 산소 결핍의 정도에 따라 질식의 증상 징후가 경미할 수도 있고 심할 수 있고 사망할 수 있다.
- 심한 질식의 전형적인 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
-
- 처음에는 피부가 창백해지거나 파래지고 잘 울지 못한다.
- 몸과 팔다리에 힘이 없어 몸이 축 늘어진다.
- 심장의 박동수가 비정상적으로 빨라지거나 늦어질 수 있다.
- 숨을 정상보다 빨리 쉬거나 느리게 쉴 수 있고 소리를 내면서 신음할 수 있다.
- 적절히 응급으로 치료하지 않으면 전신 경련을 일으키고, 더 심하면 사망한다.
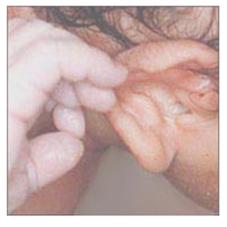
사진 209. 갓 태어난 아기의 손에 생긴 선단 청색증. 제왕 절개수술 분만으로 갓 태어난 신생아의 손에 생긴 선단 청색증.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
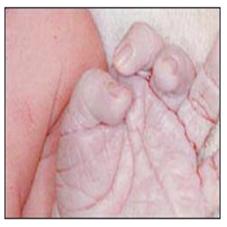
사진 210. 손에 생긴 선단 청색증
제왕 절개수술 분만으로 태어난 신생아의 손에 생긴 선단 청색증
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
| 신생아 질식의 진단 |
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 신생아가 질식됐다고 의심되면 혈중 산소농도 등을 측정해서 질식 상태가 어느 정도인지 알아볼 수 있다.
- 요즘 분만 중 태아의 심장 박동의 상태를 태아 모니터로 계속 관찰하면서 분만하는 것이 보통이다.
- 태아 모니터로 태아의 심장 박동이 정상적으로 뛰는지, 비정상적으로 뛰는지 빠른지 느린지, 규칙적인지 불규칙적인지를 자세히 정확히 알아볼 수 있다.
- 분만 중 태아가 질식 상태에 있는지 건강한지 알아볼 수 있다.
- 자궁 속에서 태변을 누면 태아가 질식 상태에 있다는 징조이다.
- 태어났을 때 아기의 아프가 점수 평가법의 총 점수를 매겨보면 생후 1분, 5분, 10분에 갓 태어난 아기의 전반적인 건강 상태가 어떠했는지도, 갓 태어난 아기가 질식됐었는지, 질식되지 않았었는지 타각적으로 알 수 있다. 아프가 점수 참조.
- 신생아가 질식되면 그 질식 상태를 응급으로 치료해 주는 것도 중요하지만 무엇 때문에 질식되었는지를 즉시 알아내든지, 적어도 추정해 그 원인을 동시 치료해 주어야 한다.
- 산소 결핍이나 기도 내 이물 등으로 산소 공급을 충분히 받지 못할 때 뇌 손상이 생기든지 사망할 수 있다.
- 기도 내 이물 등으로 막힌 기도를 열어 기도를 확보해 주고 숨을 정상적으로 쉬게 할 수 있는 시간은 극히 제한됐다.
- 기도가 막혀 숨을 쉬지 못해 산소 결핍이 생길 때, 0~4분 이내에 산소를 정상적으로 공급 받게 하면 뇌손상이 생길 가능성은 적으나 4~6분이나 그 이상 지나면 뇌 손상이 생길 가능성이 많고 6~10분 이상 지나면 뇌손상이 생길 가능성이 아주 많다.
- 신생아가 질식되지 않게 예방적 치료를 하는 것도 중요하지만 질식 상태로 들어가려고 하거나 질식 상태에 빠져 있으면 즉시 적절히 치료하는 것도 중요하다.
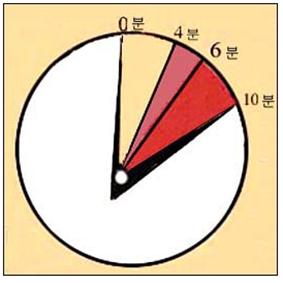
그림 211. 신생아나 신생기 이후 소아, 또는 성인이 질식됐을 때 소생시켜 살릴수 있는 데 소요될 시간이 극히 제한됐다. 0-4분 내 소생시켜야 살 수 있는 가능성이 많다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
| 신생아 질식의 치료 |
- 태아가 질식되는 원인은 앞서 열거한 것 이외 더 많이 있다.
- 모든 임신부는 안전하게 임신 분만을 할 때까지 의사의 지시에 따라 임신부가 지켜야 할 사항을 잘 지켜야 한다.
- 안전 분만 출산을 위한 산과 의료시설이 갖추어지고 분만 시 필요한 의료인이 있는 병원에서 안전하게 분만하는 것이 신생아 질식을 예방하는 데 가장 좋고, 질식이 생길 때 즉시 적절히 치료할 수 있는 방법이다.
- 병원에서도 태아나 신생아가 될 수 있는 대로 질식되지 않게 예방하기 위해 만반의 준비도 하고 전력을 다 한다.
- 신생아가 질식됐을 때는 그 원인에 관계없이 아기에게 100% 산소 호흡치료를 즉시 시작해 혈중 산소 농도를 정상 수치로 증가시키고 숨을 정상적으로 쉬게 하는 응급, 진보적 생명유지심폐소생술 치료를 한다.
- 입, 비강, 인두, 후두 속에 괸 양수, 점액, 태변, 피 등을 흡입구나 흡인기로 흡인해서 기도 속을 열어 기도를 확보해 주고 숨을 정상적으로 쉬게 즉시 처치한다.
- 원인이 무엇인지 알아보고 필요한 약물로 치료한다.
- 산소호흡치료를 시키고 기도를 깨끗하게 열어 준 후에도 신생아가 질식 상태에 있으면 질식 정도에 따라 인공호흡, 심장마사지 또는 진보적 심폐소생술 응급 치료를 하거나 그래도 심장이 잘 뛰지 않을 때에는 에피네프린 등 약물로 치료한다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료-인공호흡과 심장마사지(심폐소생술) 참조.
- 질식(가사) [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료-신생아 심폐소생술(Neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation)
|
다음은 “뇌성마비와 모야모야병과의 관계”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 뇌성마비와 모야모야병과의 관계는….
Q.
안녕하세요? 저는 4살배기 여자아이 조카를 두고 있는 고모입니다.
다름이 아니고 저희 조카가 아기 때부터 발육상태에 좀 이상한 징후를 보였거든요?
혼자 앉아있기 시작한 나이부터 술에 취한사람이 흔들거리는 것처럼 넘어지려다가 다시 일어서기를 계속 반복하고, 걷는 것도 다른 아이들보다 월등히 늦었는데, 계속 넘어지고 잘 걷지를 못하고 흔들거리고 그랬습니다. 처음에는 다른 아이들보다 좀 늦으려니…하고 생각했었는데, 정도가 지나친 것 같아서 원주에 있는 좀 큰 병원을 찾았는데, 뇌성마비검사를 다 끝내고 나서 뇌성마비는 아니니 재활의학과 치료를 받으라는 말씀이 있었습니다. 아이가 좀 커서 예전보다는 많이 나아졌지만, 아직도 잘 뛰어다니지는 못하는 상태이고, 가을경에는 다리가 아프다고 해서 가까운 병원 찾았을 때는 골반에 물이 찼다는 말씀을 하신 이 있었습니다. 그랬다가 아무래도 이상해서 재활의학과를 다시 찾았는데, 선생님말씀이 운동성뇌성마비이거나 모야모야병인 것 같다는 말씀을 하셨고, 부모는 너무 상심을 했습니다. 지금 검사받기 위해 예약을 해놓은 상태인데, 조언 좀 부탁드립니다…자세하게 말씀해주셨으면 정말 감사하겠습니다.
수고하세요.
A.
정선님
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
어떤 병을 앓고 있는지 답변을 확실히 드릴 수 없습니다.
소아청소년과로 조카를 데리고 진료 받으러 오시면 이렇게 해 보겠습니다.
진찰을 자세히 하고 12쌍 뇌신경에 어떤 이상이 있나 알아보고 소뇌, 대뇌 등에 이상이 있나 알아보고 경막하 출혈, 경막외 출혈, 뇌 내 출혈 등이 있나 알아보고 척추에 이상이 있나 알아보고
납중독 등이 있나 알아보고 근육에 어떤 질병이 있나 알아보고 근육신경에 어떤 병이 있나 알아보고 얼굴 마비, 상지 하지 마비 등이 있나 알아보고, 시력 청력 언어 구사능력이 어떤지 알아보고, 염색체에 어떤 이상이 있나 알아보겠습니다.
자녀의 성장 발육 상태와 정도를 타각적으로 검사하고 평가해보겠습니다.
임신이 정상이었나, 분만은 정상적이었나, 아프가 점수가 얼마였나, 태어나서 금방 크게 소리 내어 울었나, 산소호흡 치료가 필요했는가, 그동안 앓았던 병은 무엇인가, 그동안 한 검사는 무엇인가 그리고 그 검사결과는 어떤지, 그동안 검진했던 의사들 중 소아신경내과 전문의가 있었는지, 뇌 MRI 검사를 했는가, EEG 검사, CBC 피검사, 칼슘 혈중 농도검사, 소변검사 등등을 했었는지 했다면 그 결과는 정상인지 등을 종합해서 진단을 하고 무슨 병이었는지 감을 잡을 수 있을 것입니다.
이런 것을 해 보지도 않고 무슨 병이 있는지 없는지 답변을 드릴 수 없습니다.
도움을 더 받으시려면 이상 말씀드린 모든 검사와 검진을 하시든지 했으면 그 결과를 Email로 보내주시면 다시 답변을 드리겠습니다.
지금 이 시점에서 모야모야(Moyamoya)병인지 뇌성마비인지 알 방법이 없습니다.
질문이 더 있으면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다– 소아가정간호백과]-제12권 소아청소년 신경 정신, 정서, 행동, 수면문제–모야모야병 참조. 이상원 드림
Neonatal asphyxia 신생아 질식(신생아 가사)
- The disease that occurs before, during, immediately after delivery, or after delivery when the fetus or newborn does not receive enough oxygen for any reason is called neonatal choking, or neonatal asphyxia.
- When a newborn is severely suffocated, the brain, heart, lungs, stomach, kidneys, and other vital organs essential to basic human life can be temporarily or permanently damaged depending on the degree of suffocation.
- There are several causes of suffocation in newborns. Here, it can be broadly classified into causes before childbirth and causes after childbirth (see cerebral palsy).
1. Causes before childbirth
① When giving birth while receiving general anesthesia, When the delivery part does not receive sufficient oxygen supply, Fetuses may also become suffocated because they do not receive enough oxygen.
② A baby born to a delivery woman suffering from severe heart disease
③ During delivery while receiving spinal anesthesia, the blood pressure of the delivery part suddenly When it falls
④ The artery in the pelvic cavity of the delivery part, which supplies blood to the fetus in the uterus, is pressed against the uterus. The mother’s blood is not adequately supplied to the fetus, and oxygen supply to the fetus is thus impaired. When it’s not enough.
⑤ A uterine contracting agent is used to deliver a fast delivery so that the blood of the delivery woman is sufficient for the fetus. When it cannot be supplied.
⑥ When there is a knot in the umbilical cord and the placenta does not provide enough blood to the fetus
⑦ For other reasons
2. Causes after childbirth
- When red blood cells in the newborn’s blood are severely hemolytic, or when a newborn baby has severe anemia due to severe internal or external bleeding
- Whether a newborn baby falls into shock due to an infectious disease such as sepsis or meningitis
- When severe anemia develops,
- When intracranial bleeding occurs
- When you cannot breathe properly after having brain damage or receiving medication that harms central nervous system function
- When oxygen deficiency occurs due to severe congenital heart disease
- When a newborn baby inhales amniotic fluid, meconium, and maternal feces into the airways and the airways are blocked For other reasons

Photo 208. Medical devices and oxygen that can be used to prevent suffocation of newborns and conveniently treat them when they are suffocated, and drugs that can perform progressive cardiopulmonary resuscitation, oxygen, and delivery should be prepared at all times. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Symptoms, signs of choking(asphyxia) in newborns
- Newborn suffocation is a relatively common disease.
- Symptoms and signs differ depending on the cause and severity of suffocation, and the presence or absence of complications.
- The fetus may suffocate before or during delivery when the fetus does not receive enough blood from the mother and the oxygen concentration in the fetus’s body is abnormally low.
- A fetus that is severely suffocated in the womb can press the meconium in the amniotic fluid.
- The fetus’s heartbeat can be abnormally fast or slow, and it can be irregular. Sometimes the fetus can die in the womb.
- It can also result in suffocation when a newborn baby immediately after childbirth, or when a newborn baby thereafter, does not receive enough oxygen.
- Depending on the degree of oxygen deficiency, the signs of asphyxiation can be mild, severe, and even death.
Typical symptoms, signs of severe suffocation are:
- At first, the skin becomes pale or blue and does not cry well.
- There is no strength in the body and limbs, and the body is drooping.
- The heart rate may become abnormally fast or slow.
- Your baby can breathe faster or slower than normal, and your baby can moan while making a sound.
- Without proper emergency treatment, it can cause systemic convulsions and, worse, death.

Picture 209. Apical cyanosis on the hand of a newborn baby. Apical cyanosis on the hand of a newborn baby after cesarean section delivery. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Picture 210. Apical cyanosis on the hand of a newborn born with cesarean section delivery Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Diagnosis of asphyxiation in newborns
- If you suspect that the newborn has suffocated by taking the medical history, symptoms, signs, and examination findings, you can measure the level of oxygen in the blood to find out how much the suffocation is.
- These days, it is common to deliver while continuing to observe the state of the fetus’s heartbeat with a fetal monitor during delivery.
- With a fetal monitor, you can see in detail whether the fetus’s heartbeat is beating normally, beating abnormally, fast or slow, regular or irregular.
- During delivery, you can find out if your baby is choking or healthy.
- Pressing the meconium in the womb is a sign that the fetus is in a state of suffocation. When calculating the total score of the baby’s Apgar scoring method at birth, the overall health of the newborn baby at 1 minute, 5 minutes, and 10 minutes after birth, whether the newborn baby was suffocated, or not suffocated.
- Can be seen as. See Afga score. When a newborn is suffocated, it is important to treat the suffocating condition as an emergency, but whether to find out immediately what caused the suffocation or at least estimate the cause and treat the cause at the same time.
- Brain damage or death can occur when oxygen deficiency or a foreign body in the airways does not receive enough oxygen.
- The time to open the airway blocked by foreign objects in the airway to secure the airway and breathe normally was extremely limited.
- When oxygen deficiency occurs because the airway is blocked and you cannot breathe, if you receive oxygen normally within 0 to 4 minutes, the possibility of brain damage is less, but after 4 to 6 minutes or more, there is a high possibility of brain damage.
- After more than a minute, there is a high probability of developing brain damage. It is important to provide prophylactic treatment to prevent suffocation of the newborn, but it is also important to promptly treat the newborn if it is attempting to enter a suffocating state or is suffocated.

Figure 211. The time it takes to resuscitate a newborn child or a child or adult after suffocation when they are suffocated is extremely limited. There is a lot of possibility to survive if you must revive it within 0-4 minutes. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Treatment of suffocation in newborns
- There are many more causes of suffocation of the fetus other than those listed above. All pregnant women must follow the instructions of the doctor until the pregnancy is delivered safely and follow the instructions for the pregnant woman.
Safe delivery
- A safe delivery in a hospital equipped with obstetric medical facilities for childbirth and medical personnel required for delivery is the best way to prevent suffocation of newborns, and is a method that can be treated promptly and appropriately when suffocation occurs.
- Even in the hospital, we do everything we can to prepare and do everything in our power to prevent suffocation from becoming fetuses or newborns as much as possible.
- When a newborn is suffocated, irrespective of the cause of the suffocation, the baby is given an emergency, progressive life-sustaining cardiopulmonary resuscitation treatment that increases blood oxygen levels to normal levels and breathes normally by starting 100% oxygen breathing therapy immediately.
- Aspirate the amniotic fluid, mucus, meconium, and blood in the mouth, nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx with an inhaler or aspirator to open the airway, secure the airway, and take immediate treatment so that you can breathe normally.
- Find out what is the cause and treat it with the medications you need.
- If the newborn is in a state of suffocation even after oxygen respiration therapy is given and the airways are opened cleanly, artificial respiration, cardiac massage, or progressive cardiopulmonary resuscitation is given depending on the degree of suffocation, or if the heart is still not beating well, it is treated with drugs such as epinephrine.
- Visit www.drleepediatrics.com ]-Vol. 1 Children’s and Adolescent Emergency Medical Care-Artificial Respiration and Heart Massage (CPR). Choking (lyrics) [Parents should also be anti-doctors-Pediatrics and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Vol. 1 Emergency medical care for children and adolescents-Neonatal cardiopulmonary resuscitation
The following is an example of the Internet pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer on “the relationship between cerebral palsy and moyamoya disease”.
Q&A.
The relationship between cerebral palsy and moyamoya disease…
Q.
Good morning? I am an aunt with a nephew of a 4-year-old girl. Nothing else, because my nephew showed some strange signs of her development from the time she was a baby. From the age when I started sitting alone, a drunk person tried to fall as if shaking and then stood up again and again, and walking was much later than other children, but it kept falling, unable to walk well, and shaking. At first, I thought, “I’m going to be a little later than the other children…”, but I thought it was too much, so I went to a larger hospital in Wonju. After completing the cerebral palsy test, it was not a cerebral palsy, so I was told to seek medical treatment from the rehabilitation medicine department. . Although the child is a little bigger than before, he is still in a state of not running well, and there was someone who said that his leg hurts in the fall, so when he visited a nearby hospital, he said that his pelvis was filled with water. Then I went back to the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine because it was strange, but the teacher said that it was likely motor cerebral palsy or moyamoya disease, and my parents were so heartbroken. I have made a reservation for the test right now, but please give me some advice…I would be very grateful if you could tell me in detail. work hard.
A.
Jeong Seon-nim Good morning. Thanks for asking. That’s a good question. The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family medical history, medical examination findings, and clinical examination, the more helpful it is to give you an answer.
We will respond based on the information you provided. We can’t be sure to answer what kind of illness you have. If you come to the Pediatrics with your nephew for medical treatment, I will do this.
Examine-in detail, find out what abnormalities are in the 12 pairs of cranial nerves, find out if there is an abnormality in the cerebellum and cerebrum, find out if there are subdural hemorrhages, epidural hemorrhages, intracranial hemorrhages, etc., and find out if there are any abnormalities in the spine.
We will find out if there is lead poisoning, etc., find out what diseases are in the muscles, find out what diseases are in the muscles, find out whether there are facial paralysis, paralysis of the upper extremities, etc., find out how the ability to speak sight, hearing, language, etc., and find out what abnormalities are in the chromosomes.
Let’s examine and evaluate the child’s growth and development status and degree objectively. Was pregnancy normal, delivery was normal, and how much was the score in Afghanistan?
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.