특발성 호흡곤란 증후군(특발성 호흡장애 증후군/유리질막증), Idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome in newborn infants(IRDS)
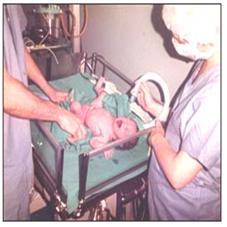
사진 307.미숙아로 태어난 신생아가 호흡곤란이 생겨 산소 튜브로 치료받고 있다. 그 후 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군을 진단받고 치료를 받았다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 아주 작은 미숙아들의 폐는 더 미숙해서 만삭에 태어난 건강한 신생아들의 폐에 비해서 생리적‧기능적으로 특이한 점이 많다. 수정체 후 섬유증식증 참조.
- 미숙아 폐기포(肺氣胞/폐포) 내에 서팩탄트(표면활성제/Surfactant)라는 생화학적 물질이 정상적으로 충분히 들어 있지 않다.
- 폐포와 세기관지(細氣管支/모세기관지)도 더 미숙하고 그 기능도 미숙하다.
- 흡입된 공기 속 산소와 몸속에 생긴 이산화탄소가 미숙아의 폐포에서 적절히 잘 교환되지 않다.
- 이런 여러 가지 이유로 특히 아주 작은 미숙 신생아의 폐에 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군 등 여러 가지 병이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 폐가 미숙하기 때문에 생기는 병들 중 유리질막증(특발성 호흡곤란 증후군)이 미숙 신생아에게 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
- 과거에는 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군은 미숙아들의 사망의 주원이다.
- 임신 28주 이전 태어난 미숙 신생아들의 60%, 임신 32~36주 사이에 태어난 미숙 신생아들의 15∼20%, 임신 37주 이후 태어난 신생아들의 5%에게 이 병이 생겼었다는 연구도 있다.
- 그러나 임신 38주 이후에 태어난 건강한 만삭 신생아들은 이 병에 거의 걸리지 않는다.
- 요즘 이 병에 걸리는 신생아의 수가 전에 비해 많이 줄어들었다.
- 이 병은 잘 치료해 주면 거의 회복되는 것이 보통이다.
- 1형 당뇨병을 앓는 임신부에게 태어난 미숙 신생아들이나 제왕절개수술 분만으로 태어난 미숙아신생아들에게 이 병이 더 잘 생길 수 있다.
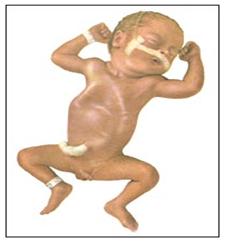
그림 308.특발성 호흡곤란 증후군이 아주 심하면 그로 인해 이 정도로 심한 호흡곤란이 생길 수 있다. 복벽과 흉곽 벽이 심하게 수축되어 흉곽 복벽 함몰 현상이 생겼다. 이런 호흡곤란 징후는 신생아 폐렴이 있을 때도 생길 수 있다.
Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216 Division of Laboratories, USA 과 소아가정간호백과
| 신생아 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군 증상 징후 |
- 이 병의 정도, 합병증, 미숙 신생아의 체중 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 이 병에 걸리면 미숙 신생아나 만삭 신생아에게 출생 후 곧 다음과 같은 여러 가지 증상 징후가 나타나는 것이 보통이다.
- 1분에 60번 이상 숨을 자주 쉬는 것이 보통이고 때로는 1분에 60∼120회 정도 자주 쉬기도 한다.
- 심한 경우 생후 곧 질식 상태에 빠질 수 있다.
- 피부가 창백하고 파래질 수 있다.
- 전신 청색증이 나타날 수 있다.
- 숨 쉴 때마다 신음소리를 내기도 하고,
- 특히 숨을 내쉴 때마다 그런팅(Grunting/그렁거림) 호흡을 하고
- 주위 사람이 그런팅 호흡소리를 맨 귀로 들을 수 있고
- 청진기로도 들을 수도 있다.
- 비익이 숨 쉬는 대로 벌렁거리기도 한다.
- 숨 쉴 때마다 가슴 늑골 사이(늑간)에 있는 늑골 근육이 흉강 속 쪽으로 빨려 들어갔다 나왔다 할 때도 있다.
- 늑골 하 근육이 흉강 속 쪽으로 빨려 들어갔다 나왔다 할 수도 있고 늑골상위 근육도 흉강 속 쪽으로 빨려 들어갔다 나왔다 할 때도 있다(사진 308참조).
- 젖꼭지나 인공영양 젖병 꼭지를 제대로 빨지도 못한다.
- 이 때 혈중 산소 농도는 정상 이하로 낮고(보통 PaO2가 55mm Hg이다),
- 이산화탄소의 농도가 정상 이상으로 증가된다.
- 이 병이 심할 때 조속히 적절하게 치료하지 않으면 생후 24∼48시간 이내에 호흡부전증 등으로 사망할 수 있다.
| 신생아 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군의 진단 치료 |
- 병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 가슴 X선 사진을 찍어 진단한다.
- 선천성 후비공 폐쇄증, 기관 협착증, 기관지 협착증, 설 갑상선, 태변 흡인증, 일시적 빈호흡증, 박테리아 폐렴 또는 바이러스 폐렴, 기흉, 무기폐, 폐 발육부전, 선천성 심장 기형, 선천성 횡격막 허니아, 다 적혈구증, 기관 식도누관(루), 두개강 내 출혈, 심낭 기흉증, 저 혈당증, 산혈증, 신생아 가사증, 또는 쇼크 등으로 생긴 증상 징후와 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군으로 생긴 증상 징후가 비슷할 때도 있다. 그런 병들과 감별 진단해야 한다.
- 가슴 X선 사진, 초음파 검사, MRI 검사, Xenon 스캔 검사, 심장 에코그람검사, 동맥혈 가스검사, 혈청 포도당 검사, CBC 피 검사, 그 외 다른 적절한 검사를 해서 진단한다.
- 10% 포도당 전해질용액 혈관주사로 수분과 영양분을 공급해 준다.
- 여러 가지 방법으로 산소호흡 치료를 하고 체온을 보온한다.
- 때로는 기관 내 내관 삽입치료를 한다.
- 기관 속에 기관 내 내관을 넣고 그 관을 통해 산소호흡 치료를 하기도 한다.
- 산소호흡 치료를 할 때 옥시메터 검사나 동맥혈 피검사로 혈중 산소 농도를 수시로 측정한다.
- 요즘 옥시메터 기구로 피를 뽑지 않고 혈중 산소 농도를 손가락 등에서 쉽게 측정할 수 있다.
- 임신 32주 이후 출생한 비교적 큰 미숙아들은 적절히 치료를 받으면 이 병에서 거의 다 회복될 수 있다.
- 이 병을 앓는 중 저산소증, 저 혈당증, 빈혈, 기흉, 무기폐 등의 합병증이 생길 수 있다.
- 이 병은 항생제로 치료되지 않으나 서팩탄트제(표면활성제) 등으로 치료할 수 있다.
Update, 4/2021 Pediatrics
신생아 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군의 정도를 폐 울트라사운드코아 방법으로 알아볼 수 있다. Update,
4/2021, Pediatrics
The degree of neonatal idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome can be assessed using the lung ultrasound core method.
Idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome in newborn infants (IRDS) 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군(특발성 호흡장애 증후군/유리질막증)

Picture 307: A newborn baby born prematurely has difficulty breathing and is being treated with an oxygen tube. After that, idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome was diagnosed and treated. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- The lungs of very small premature babies are more immature and have many physiological and functional characteristics compared to the lungs of healthy newborns born at term.
- See Post lens fibrosis. The biochemical substance called surfactant (surfactant) is not normally sufficiently contained in the alveolar vesicles of premature infants.
- The alveoli and bronchioles (細氣管支 capillary bronchi) are also more immature and their function is immature.
- Oxygen in the inhaled air and carbon dioxide generated in the body are not properly exchanged in the alveoli of premature babies.
- For a number of these reasons, a number of diseases, including idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome, are more likely to develop in the lungs of very small, immature newborns.
- Among the diseases caused by immature lungs, vitreous membranes (idiopathic dyspnea syndrome) are more likely to occur in immature newborns.
- In the past, idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome was the leading cause of death in premature babies. There are studies showing that 60% of premature newborns born before 28 weeks of gestation,15 to 20% of premature newborns born between 32 and 36 weeks of gestation, and 5% of newborns born after 37 weeks of gestation developed the disease.
- However, healthy full-term newborns born after 38 weeks of gestation rarely get the disease.
- These days, the number of newborns with this disease has decreased significantly compared to before.
- It is common for this disease to almost recover if treated well.
- The disease may be more prevalent in premature newborns born to pregnant women with type 1 diabetes, or premature newborns born with cesarean section.

Figure 308. If idiopathic dyspnea syndrome is very severe, it can lead to such severe dyspnea.
The abdominal wall and thoracic wall contracted severely, resulting in a depression of the thoracic abdominal wall. These signs of dyspnea can also occur with neonatal pneumonia.
Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216 Division of Laboratories, USA Department of Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia
Symptoms, signs of Idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome in newborn infants(IRDS)
- Symptoms and signs differ depending on the severity of the disease, complications, and the weight of an immature newborn baby.
- it is common for immature newborns or full-term newborns to develop a number of symptoms soon after birth.
- It is common to breathe more than 60 times a minute often, and sometimes 60 to 120 times a minute.
- In severe cases, it can lead to suffocation soon after birth.
- The skin may be pale and blue.
- Systemic cyanosis may develop.
- Whenever he breathes, he moans, Especially when I exhale, he breathes grunting.
- People around him can hear the breathing sound of grunting with bare ears.
- You can also listen with a stethoscope.
- As the breathes, the alna nasi may flutter.
- Whenever he breathes, the rib muscles between the ribs of the chest (intercostal) are sucked into the chest cavity and come out.
- In some cases, the sub-costal muscles are sucked in and out of the chest cavity, and the upper ribs are also sucked in and out of the chest cavity. They can’t suck the nipples or bottle nipples properly.
- At this time, the oxygen concentration in the blood is lower than normal (usually PaO2 is 55mm Hg), The concentration of carbon dioxide increases beyond normal.
- If this disease is severe and not treated promptly and appropriately, death may occur from respiratory failure within 24 to 48 hours after birth.
Diagnosis, treatment of Idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome in newborn infants(IRDS)
- Comprehensive medical history, symptoms, medical findings, etc.
- If this disease is suspected, a chest X-ray, lung ultrasound is taken for diagnosis.
- Congenital posterior nostril obstruction, tracheal stenosis, bronchial stenosis, glandular thyroid, meconium aspiration, transient tachypnea, bacterial pneumonia or viral pneumonia, pneumothorax, atelectasis, pulmonary hypoplasia, congenital heart malformation, congenital diaphragmatic hernia, polycythemia vera, tracheoesophageal fistula, intracranial hemorrhage, pericardial pneumothorax, hypoglycemia, acidemia, or shock may be similar to those caused by idiopathic dyspnea syndrome.
- You have to diagnose differently from those diseases.
- Diagnosis is performed by chest X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, Xenon scan, cardiac echogram, arterial blood gas test, serum glucose test, CBC blood test, and other appropriate tests.
- It supplies moisture and nutrients by vascular injection of 10% glucose electrolyte solution.
- There are several ways to treat oxygen breathing and keep your body warm.
- Sometimes endotracheal tube insertion treatment is performed. An inner tube inside the trachea is inserted into the trachea, and oxygen breathing treatment is performed through the tube.
- When oxygen respiration treatment is performed, the oxygen concentration in the blood is often measured with an oximeter test or an arterial blood test.
- These days, the oxygen concentration in the blood can be easily measured from a finger, etc. without drawing blood with an oximeter device.
- Relatively large premature babies born after 32 weeks of gestation can recover from the disease with appropriate treatment. While suffering from this disease, complications such as hypoxia, hypoglycemia, anemia, pneumothorax, and atelectasis may occur.
- This disease is not treated with antibiotics, but can be treated with a surfactant drug (surface active agent).
Update, 4/2021 , Pediatrics
신생아 특발성 호흡곤란 증후군의 정도를 폐 울트라사운드코아 방법으로 알아볼 수 있다.
Update, 4/2021, Pediatrics The degree of neonatal idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome can be assessed using the lung ultrasound method.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.