미숙 신생아의 기흉, Pneumothorax in premature infants
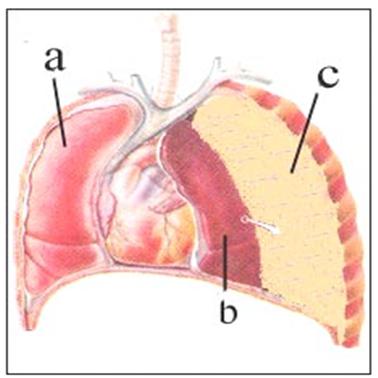
그림 310.장력성 기흉. a-정상 폐, b-기흉으로 쪼그라진 폐, c-기흉.
Used with permission from Ross Labotories,Columbus, Ohio, USA 소아가정간호백과
- 미숙한 폐포나 모세기관지 등의 일부가 터지거나 폐의 일부가 찢어질 때, 기관지 속이나 모세기관지 속, 또는 폐포 속 등에서 공기가 늑막강(흉막 강) 속으로 새어 들어갈 수 있다.
- 이 때 늑막강 속에 공기가 차 있는 병을 기흉이라고 한다.
- 기흉은 장력성 기흉, 이차성 기흉, 자연 기흉 등으로 분류될 수 있다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다- 소아가정간호백과]-제 8권 소아 호흡기 질환-기흉 참조.
| 미숙 신생아 기흉의 원인 |
- 기흉은 미숙 신생아들에게도 더 쉽게 생길 수 있다.
- 만삭 신생아들에게도 생길 수 있고 신생아기 이후 소아들이나 성인들에게도 생길 수 있는 호흡기 질환이다.
- 무슨 이유로든 공기가 폐포 속에 비정상적으로 과도히 많이 차 있을 때나 폐포 속의 공기의 압력이 비정상적으로 높을 때, 또는 폐포에 어떤 이상이 있을 때, 심폐소생술 치료를 받았을 때 인공호흡으로 폐포가 터질 수 있다.
- 터진 폐포 속에서 나온 공기가 늑막강 속으로 들어가면 기흉이 생긴다.
- 아무 원인도 없이 생기는 기흉을 자연 기흉이라고 한다.
- 폐렴, 기낭, 외상, 태변 흡인 폐렴 등의 폐병으로 생긴 기흉을 이차성 기흉이라고 한다.
- 기흉이 있는 늑막강 내 압이 폐포 내 기압이나 대기의 기압보다 더 높을 때는 기흉이 있는 쪽 폐가 쪼그라져서 그 쪽 폐에 무기폐가 생길 수 있다. 이런 기흉을 장력성 기흉(張力性氣胸)이라고 한다.
- 장력성 기흉이 있을 때는 그 기흉으로 인해 흉강 내 폐, 심장과 그 외 다른 여러 기관이 본 위치에서 그 주위에 있는 다른 위치로 밀려갈 수 있다.
| 미숙 신생아 기흉의 증상 징후 |
- 기흉의 정도와 종류, 원인 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 기흉이 경미하고 장력성이 아닐 때는 아무런 증상 징후가 없을 수 있다.
- 장력성 기흉이나 좀 더 심한 기흉이 있을 때는 흉강 내 폐나 심장, 또는 다른 기관들이 본 위치에서 주위 다른 위치로 밀려가기도 하고 그로 인해 다음과 같은 여러 가지 증상 징후가 나타날 수 있다.
- 호흡곤란이 생기고, 숨결이 빠르고 맥박이 빨라지고 피부가 창백해지고 몹시 아파보일 수 있다.
- 원인을 확실히 알 수 없이 자연적으로 생긴 작은 자연 기흉이 있을 때는 아무런 증상 징후가 나타나지 않을 때가 많다.
- 이런 자연 기흉을 신생아들에게 흔히 볼 수 있다.
- 그들이 어떤 병을 앓고 있을 때 그 병을 진단하기 위해 가슴 X선 사진검사를 했을 때 우연히 자연 기흉이 발견되기도 한다.
| 미숙 신생아 기흉의 진단 치료 |
- 병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합하여 이 병이 의심되면 가슴 X선 사진으로 진단한다.
- 기흉이 경미하고 자연 기흉이 있을 때는 조심스럽게 관찰하면서 100% 산소호흡 치료를 하면 대개는 잘 낫는다.
- 이 때 늑막강 속에 있는 공기가 자연히 흡수되어 자연 기흉이 치료된다.
- 장력성 기흉으로 기관·기관지·모세기관지·폐포 속의 공기가 그 장력성 기흉이 있는 늑막강 속으로 계속 흘러 들어가기 때문에 장력성 기흉으로 그 쪽 폐의 일부 또는 전부가 쪼그라들 수 있고 그쪽 폐에 일부 또는 전부에 무기폐가 생길 수 있다.
- 이 때 기흉으로 생긴 늑막강 공기를 큰 주사 바늘 등으로 뽑아 치료하기도 하고
- 작은 관을 기흉이 있는 늑막강 속에 넣어 그 관을 통해 늑막강 속에 찬 공기를 빼서 치료하기도 한다.
- 기흉을 일으킨 원인에 따라 치료한다.
|
다음은 “신생아 패혈증, 신생아 기흉”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 신생아 패혈증, 신생아 기흉
Q.
안녕하세요. 궁금하고 걱정되는 사항이 있어서 글을 올립니다.
태어난 지 2시간 만에 호흡이 곤란하고 맥박이 빨라서 출생한 병원에서 추천하여 종합병원으로 입원한 신생아의 아빠입니다.
출생 후 12시간쯤, 입원한 병원에서는 패혈증으로 추정하여 항생제를 투여하고 균을 배양하여 검사를 하고 있습니다.
결과를 기다리던 중 출생 후 22시간경에 기흉이 발생하여 오른쪽 갈비뼈 쪽으로 튜브를 삽입하여 공기를 빼고 있는 중입니다.
제가 궁금한 것은 패혈증으로 추정되는 상황과 기흉이 발생된 상황에서 저희 아기의 구체적인 병명이 궁금합니다. 이상원 선생님이 적어 놓은 글을 보며, 각 증상징후가 관련이 없는 것 같은데, 출생 후 24시간이 안된 제 자식에게는 같이 발생하였기에, 과연 제 자식의 병명이 무엇이고 앞으로 어떻게 악화될지 너무나 궁금하고 걱정이 되어 글을 올립니다.
넓고 깊은 안목으로 고견을 부탁합니다.
도움이 되는 글, 꼭 부탁합니다.
A.
신생아 아빠께
안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거와 가족의 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 결과 등 자세한 정보가 있으면 답변을 드리는 데 많은 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 참작해 답변을 드립니다.
지금 바로 먼저 들어온 질문에 답변을 하던 중 이 질문을 받고 답변을 드립니다.
기다리고 기다렸던 아기의 탄생을 축하드립니다. 그리고 걱정을 많이 하시는 부모님들께 죄송스럽습니다.
임신 분만에 관한 정보도 모르고, 진찰하지 않고 아무 임상검사의 결과도 모르면서 답변을 드리는 것이 부적절합니다.
고명하신 자녀의 의사 선생님이 계신데 어떻게 답변을 드릴 수 있을까 당황스럽습니다.
신생아의 피부색이 정상이 아니어도, 숨을 비정상적으로 빠르게 쉬어도, 맥박이 비정상적으로 빨라도 어딘가 아픈 것같이 보여도 신생아가 패혈증에 걸렸나 의심해 보는 것이 일반적입니다.
아무런 원인을 찾을 수 없이 생긴 기흉은 일차성 기흉이라고도 하고 자연 기흉이라고도 합니다.
폐렴이나 특발성 호흡곤란 중후군(유리질막증) 등이 있을 때 그런 병과 같이 생긴 기흉을 이차성 기흉이라고 합니다.
경미한 기흉, 긴장성 기흉 등 여러 종류의 기흉이 있습니다.
그 원인에 따라서 치료할 수 있습니다.
패혈증과 기흉이 직접 관련이 되어 있을 수도 있고 아무 관련성이 없을 수도 있습니다.
어디까지나 담당 의사께 질문을 하십시오.
직접 질문하시고 답변을 구하시는 것이 좋습니다.
아무쪼록 빨리 회복되기를 빌겠습니다.
질문이 더 있으면 또 방문하세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Pneumothorax in premature infants 미숙 신생아의 기흉

Fig. 310 Tenson pneumothorax. a-normal lung, b-pneumothorax, c-pneumothorax. Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio, USA Pediatric Home Nursing Encyclopedia
- When a part of an immature alveolar or capillary bronchus breaks or a part of the lungs is torn, air may leak into the pleural cavity (pleural cavity) from the inside of the bronchi, capillary bronchi, or alveoli.
- At this time, a disease filled with air in the pleural cavity is called a pneumothorax. Pneumothorax can be classified into a tension pneumothorax, secondary pneumothorax, and natural pneumothorax.
- Visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Vol. 8 Children’s Respiratory Diseases-Refer to Pneumothorax.
Causes of pneumothorax in premature newborns
- Pneumothorax is more likely to develop even in premature newborns.
- It is a respiratory disease that can occur in full-term newborns as well as in children and adults after the neonatal period.
- The alveoli may burst with artificial respiration when for any reason the air is abnormally overfilled in the alveoli, when the air pressure in the alveoli is abnormally high, or when there is an abnormality in the alveoli, or when receiving CPR treatment.
- When air from the open alveoli enters the pleural cavity, a pneumothorax occurs.
- A pneumothorax that occurs without any cause is called a natural pneumothorax. Pneumothorax caused by lung diseases such as pneumonia, air sac, trauma, meconium aspiration pneumonia, etc. is called secondary pneumothorax.
- When the pressure in the pleural cavity where the pneumothorax is located is higher than the air pressure in the alveolar or the atmosphere, the lung on the side of the pneumothorax may become crushed, resulting in atelectasis in that side.
- This pneumothorax is called tension pneumothorax (張力性氣胸).
- When you have a tension pneumothorax, the pneumothorax can cause the lungs, heart, and other organs in the chest cavity to be pushed from a natural position to another position around it.
Symptoms, signs of pneumothorax in premature newborns
- Symptoms and signs differ depending on the severity, type, and cause of pneumothorax.
- When the pneumothorax is mild and non-tensile, there may be no signs of symptoms.
- In the case of a tension pneumothorax or more severe pneumothorax, the lungs, heart, or other organs in the chest cavity may be pushed from one location to another location around the chest cavity, resulting in a number of symptoms, including: Difficulty breathing, quick breathing, quick pulse, pale skin and can look terribly painful.
- When there is a small, spontaneous pneumothorax that occurs without a clear cause, there are often no symptoms, signs.
- This natural pneumothorax is common in newborns.
- When they are suffering from a certain disease, a spontaneous pneumothorax is discovered accidentally when a chest x-ray is performed to diagnose the disease.
Diagnostic treatment of pneumothorax in immature neonates
- Comprehensive medical history, symptoms, medical findings, etc.
- If this disease is suspected, it is diagnosed with a chest X-ray. If the pneumothorax is mild and there is a natural pneumothorax, it is usually healed by taking 100% oxygen breathing treatment while carefully monitoring it.
- At this time, the air in the pleural cavity is naturally absorbed and natural pneumothorax is treated.
- Because of the tension pneumothorax, the air in the trachea, bronchi, capillary bronchi, and alveoli continues to flow into the pleural cavity where the tension pneumothorax is located. It can lead to atelectasis in all.
- At this time, the air in the pleural cavity caused by pneumothorax is extracted with a large needle, etc.
- A small tube is put into the pleural cavity where the pneumothorax is located, and through the tube, the air is removed from the pleural cavity to be treated.
- Treat it according to the cause of the pneumothorax.
The following is an example of the online pediatric and adolescent health counseling question and answer on “neonatal sepsis, newborn pneumothorax”. Q&A.
Sepsis in newborns, pneumothorax in newborns
Q.
Good morning. I have questions and concerns, so I am posting. He is the father of a newborn baby, recommended by the hospital where he was born, and admitted to a general hospital because he has difficulty breathing and has a fast pulse after 2 hours of birth. About 12 hours after birth, the hospital in which you were admitted is presumed to be sepsis, administering antibiotics, and culturing the bacteria for testing. While waiting for the result, a pneumothorax occurred around 22 hours after birth, and the tube was inserted into the right rib to remove air.
What I am curious about is the specific disease name of my baby in a situation where it is presumed to be sepsis and a situation where a pneumothorax has occurred. Looking at the writing written by Mr. Sang-Won Lee, each symptom and symptom seems to be irrelevant, but it occurred to my child less than 24 hours after birth, so I was very curious and worried about what my child’s illness was and how it would worsen in the future. Post a post. I ask for your opinion with a broad and deep perspective. Any helpful articles, please.
A.
Newborn Dad Good morning.
Thank you for asking. If you have detailed information such as the child’s age, gender, past and family medical history, medical opinions, and clinical test results, it will be very helpful to give you an answer.
We will respond by taking the information you provided into consideration. We are answering this question and answering it right now while we are answering the first question. Congratulations on the birth of the baby you have been waiting for. And I am sorry for the parents who worry a lot. It is inappropriate to give an answer without knowing the information about pregnancy or delivery, without having to consult and without knowing the results of any clinical tests.
I have a famous child’s doctor, and I am puzzled how I can give you an answer. It is common to suspect that the newborn has sepsis, even if the newborn’s skin color is not normal, even if he breathes abnormally quickly, or if his pulse is abnormally fast, but even if it looks like something hurts.
A pneumothorax that develops without finding any cause is sometimes called a primary pneumothorax or a spontaneous pneumothorax.
A pneumothorax that develops like such a disease when there is pneumonia or idiopathic respiratory distress severe group (vital dystrophy) is called secondary pneumothorax. There are several types of pneumothorax, such as mild pneumothorax and tonic pneumothorax.
Depending on the cause, it can be treated. Sepsis and pneumothorax may or may not be directly related. Just ask questions to your doctor.
We recommend asking yourself questions and asking for answers. I wish you a quick recovery. If you have more questions, please visit again. Thank you. Lee Sang-won dream
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.